H5N1 outbreaks and enzootic influenza
- PMID: 16494709
- PMCID: PMC3291402
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1201.051024
H5N1 outbreaks and enzootic influenza
Abstract
Ongoing outbreaks of H5N1 avian influenza in migratory waterfowl, domestic poultry, and humans in Asia during the summer of 2005 present a continuing, protean pandemic threat. We review the zoonotic source of highly pathogenic H5N1 viruses and their genesis from their natural reservoirs. The acquisition of novel traits, including lethality to waterfowl, ferrets, felids, and humans, indicates an expanding host range. The natural selection of nonpathogenic viruses from heterogeneous subpopulations co-circulating in ducks contributes to the spread of H5N1 in Asia. Transmission of highly pathogenic H5N1 from domestic poultry back to migratory waterfowl in western China has increased the geographic spread. The spread of H5N1 and its likely reintroduction to domestic poultry increase the need for good agricultural vaccines. In fact, the root cause of the continuing H5N1 pandemic threat may be the way the pathogenicity of H5N1 viruses is masked by co-circulating influenza viruses or bad agricultural vaccines.
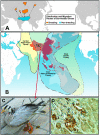
Figures

References
-
- Wright PF, Webster RG. Orthomyxoviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. p. 1533–79.
-
- Shortridge KF. Pandemic influenza: a zoonosis? Semin Respir Infect. 1992;7:11–25. - PubMed
-
- Tang X, Tian G, Zhao J, Zhou KY. Isolation and characterization of prevalent strains of avian influenza viruses in China [article in Chinese]. Chin J Anim Poult Infect Dis. 1998;20:1–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
