Novel human metapneumovirus sublineage
- PMID: 16494734
- PMCID: PMC3291390
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1201.050772
Novel human metapneumovirus sublineage
Abstract
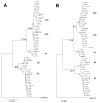
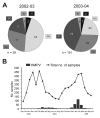
In a pediatric surveillance network, 287 (5.1%) of 5,580 specimens from patients with acute respiratory infections tested positive for human metapneumovirus (HMPV). Phylogenetic analysis of N- and F-gene sequences of identified HMPV showed that 30% belonged to a novel phylogenetic cluster.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic diversity and molecular evolution of the major human metapneumovirus surface glycoproteins over a decade.J Clin Virol. 2013 Nov;58(3):541-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.08.029. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Clin Virol. 2013. PMID: 24041471
-
Genotype variability of human metapneumovirus, South Korea.J Med Virol. 2008 May;80(5):902-5. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21129. J Med Virol. 2008. PMID: 18360903
-
Molecular epidemiology of human metapneumovirus in Ireland.J Med Virol. 2008 Mar;80(3):510-6. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21081. J Med Virol. 2008. PMID: 18205227
-
Detection of genetic lineages of human metapneumovirus in Croatia during the winter season 2005/2006.J Med Virol. 2008 Jul;80(7):1282-7. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21196. J Med Virol. 2008. PMID: 18461619
-
[Human metapneumovirus].Med Clin (Barc). 2005 Oct 15;125(13):504-7. doi: 10.1157/13080214. Med Clin (Barc). 2005. PMID: 16238929 Review. Spanish. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Human metapneumovirus associated with community-acquired pneumonia in children in Beijing, China.J Med Virol. 2013 Jan;85(1):138-43. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23438. Epub 2012 Oct 23. J Med Virol. 2013. PMID: 23097275 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, evolution and transmission of human metapneumovirus in Guangzhou China, 2013-2017.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 1;9(1):14022. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50340-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31575919 Free PMC article.
-
Re-Emergence of HMPV in Gwangju, South Korea, after the COVID-19 Pandemic.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 4;12(10):1218. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12101218. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37887734 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of human metapneumovirus detected in patients with lower respiratory tract infection in upper egypt.Int J Microbiol. 2014;2014:290793. doi: 10.1155/2014/290793. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Int J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24669221 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of human metapneumovirus in children with acute lower respiratory infection in Changsha, China.J Med Virol. 2013 Mar;85(3):546-53. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23501. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Med Virol. 2013. PMID: 23296388 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
