Bartonella quintana characteristics and clinical management
- PMID: 16494745
- PMCID: PMC3373112
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1202.050874
Bartonella quintana characteristics and clinical management
Abstract
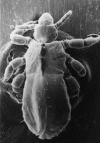
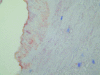
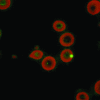
Bartonella quintana, a pathogen that is restricted to human hosts and louse vectors, was first characterized as the agent of trench fever. The disease was described in 1915 on the basis of natural and experimental infections in soldiers. It is now recognized as a reemerging pathogen among homeless populations in cities in the United States and Europe and is responsible for a wide spectrum of conditions, including chronic bacteremia, endocarditis, and bacillary angiomatosis. Diagnosis is based on serologic analysis, culture, and molecular biology. Recent characterization of its genome allowed the development of modern diagnosis and typing methods. Guidelines for the treatment of B. quintana infections are presented.
Figures



References
-
- Byam W, Carroll JH, Churchill JH, Dimond L, Sorapure VE, Wilson RM, et al. Trench fever. Oxford (UK): Oxford University Press; 1919.
-
- McNee JW, Renshaw A, Brunt EH. "Trench fever": a relapsing fever occurring with the British forces in France. BMJ. 1916;12:225–34. 10.1136/bmj.1.2876.225 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
