Global socioeconomic impact of cystic echinococcosis
- PMID: 16494758
- PMCID: PMC3373106
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1202.050499
Global socioeconomic impact of cystic echinococcosis
Abstract
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is an emerging zoonotic parasitic disease throughout the world. Human incidence and livestock prevalence data of CE were gathered from published literature and the Office International des Epizooties databases. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) and monetary losses, resulting from human and livestock CE, were calculated from recorded human and livestock cases. Alternative values, assuming substantial underreporting, are also reported. When no underreporting is assumed, the estimated human burden of disease is 285,407 (95% confidence interval [CI], 218,515-366,133) DALYs or an annual loss of US $193,529,740 (95% CI, $171,567,331-$217,773,513). When underreporting is accounted for, this amount rises to 1,009,662 (95% CI, 862,119-1,175,654) DALYs or US $763,980,979 (95% CI, $676,048,731-$857,982,275). An annual livestock production loss of at least US $141,605,195 (95% CI, $101,011,553-$183,422,465) and possibly up to US $2,190,132,464 (95% CI, $1,572,373,055-$2,951,409,989) is also estimated. This initial valuation demonstrates the necessity for increased monitoring and global control of CE.
Figures
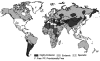
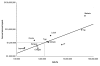
References
-
- Chai JJ. Epidemiological studies on cystic echinococcosis in China—a review. Biomed Environ Sci. 1995;8:122–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
