Parent attention versus distraction: impact on symptom complaints by children with and without chronic functional abdominal pain
- PMID: 16495006
- PMCID: PMC3232036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.12.020
Parent attention versus distraction: impact on symptom complaints by children with and without chronic functional abdominal pain
Abstract
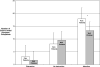
The objective of this study was to assess the impact of parent attention and distraction on symptom complaints by children with and without chronic functional abdominal pain. The water load symptom provocation task was used to induce visceral discomfort in pediatric patients with abdominal pain (N=104) and well children (N=119), ages 8-16 years. Parents were randomly assigned and trained to interact with their children according to one of three conditions: Attention, Distraction, or No Instruction. Children's symptom complaints and parents' responses were audiotaped and coded. Children completed a self-report measure of gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms before and after interacting with their parents. Parents' and children's perceptions of their interaction were assessed. Compared to the No Instruction condition, symptom complaints by pain patients and well children nearly doubled in the Attention condition and were reduced by half in the Distraction condition. The effect of attention on symptom complaints was greater for female pain patients than for male patients or well children. Findings for self-report GI symptoms were similar to those for audiotaped symptom complaints. Both pain patients and well children in the Distraction condition rated parents as making them feel better compared to ratings for the Attention condition. Parents of pain patients rated distraction as having greater potential negative impact on their children than attention. Parents' responses to children's symptom complaints can significantly increase or decrease those complaints. Girls with functional abdominal pain are particularly vulnerable to the symptom-reinforcing effects of parental attention.
Figures


Comment in
-
Effects of parent attention versus distraction on abdominal discomfort in children: a new method and new findings.Pain. 2006 May;122(1-2):8-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2006.02.004. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Pain. 2006. PMID: 16540247 No abstract available.
References
-
- Adelman AM, Revicki DA, Magaziner J, Hebel R. Abdominal pain in an HMO. Fam Med. 1995;27:321–5. - PubMed
-
- Bakeman R. Behavioral observation and coding. In: Reis HT, Judd CM, editors. Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology. Cambridge University Press; New York: 2000.
-
- Bandura A. Social learning theory. Prentice-Hall; Englewood Cliffs, NJ: 1977.
-
- Blount RL, Bachanas PJ, Powers SW, Cotter MC, Franklin A, Chaplin W, et al. Training children to cope and parents to coach them during routine immunizations: effects on child, parent, and staff behaviors. Behav Ther. 1992;23:689–705.
-
- Blount RL, Cohen LL, Frank NC, Bachanas PJ, Smith AJ, Manimala MR, et al. The Child-Adult Medical Procedure Interaction Scale – Revised: an assessment of validity. J Pediatr Psychol. 1997;22:73–88. - PubMed

