Medium plays a role in determining expression of acrB, marA, and soxS in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 16495271
- PMCID: PMC1426439
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.50.3.1071-1074.2006
Medium plays a role in determining expression of acrB, marA, and soxS in Escherichia coli
Abstract
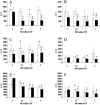
Analysis of expression of acrB, marA, and soxS in rich and minimal media, at early and late logarithmic growth phases, showed that acrB had increased expression in minimal medium compared to rich medium, but expression decreased dose dependently upon exposure to ciprofloxacin.
Figures
References
-
- Andrews, J. M. 2001. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 48(Suppl. 1):5-16. - PubMed
-
- Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

