Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E by converging signaling pathways during metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression
- PMID: 16495443
- PMCID: PMC6674817
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5196-05.2006
Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E by converging signaling pathways during metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression
Abstract
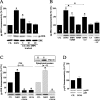
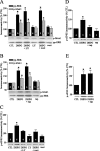
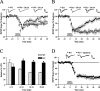
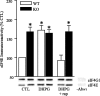
Long-term depression (LTD) is an activity-dependent decrease in synaptic efficacy that can be induced in hippocampal area CA1 by pharmacological application of the selective group I metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) agonist 3,5-diyhroxyphenylglycine (DHPG). Recent work has demonstrated that DHPG-induced LTD recruits at least two signal transduction pathways known to couple to translation, the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. However, it remains unclear which translation factors are engaged by these two signaling pathways during mGluR-LTD. In this study, we investigated whether the group I mGluRs couple to the cap-dependent translation proteins: Mnk1, eIF4E, and 4E-BP. We found that both the MEK-ERK and PI3K-mTOR signaling pathways are critical for the DHPG-induced regulation of these translation factors. Furthermore, we demonstrate that increasing eIF4F complex availability via the genetic elimination of 4E-BP2 can enhance the degree of LTD achieved by DHPG application in an ERK-dependent manner. Our results provide direct evidence that cap-dependent translation is engaged during mGluR-LTD and demonstrate that the MEK-ERK and PI3K-mTOR signaling pathways converge to regulate eIF4E activity after induction of DHPG-LTD.
Figures


References
-
- Banko JL, Hou L, Klann E (2004). NMDA receptor activation results in PKA- and ERK-dependent Mnk1 activation and increased eIF4E phosphorylation in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurochem 91:462–470. - PubMed
-
- Bell KA, O’Riordan KJ, Sweatt JD, Dineley KT (2004). MAPK recruitment by beta-amyloid in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures depends on physical state and exposure time. J Neurochem 91:349–361. - PubMed
-
- Bolshakov VY, Siegelbaum SA (1994). Postsynaptic induction and presynaptic expression of hippocampal long-term depression. Science 264:1148–1152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
