CD40 restrains in vivo growth of Toxoplasma gondii independently of gamma interferon
- PMID: 16495528
- PMCID: PMC1418638
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1573-1579.2006
CD40 restrains in vivo growth of Toxoplasma gondii independently of gamma interferon
Abstract
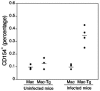
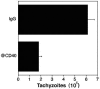
CD40-CD154 interaction is pivotal for resistance against numerous pathogens. However, it is not known if this pathway can also enhance in vivo resistance in gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-deficient hosts. This is an important question because patients and mice with defects in type 1 cytokine response can control a variety of pathogens. While blockade of endogenous CD154 resulted in a remarkable increase in parasite load in IFN-gamma-/- mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii, in vivo administration of a stimulatory anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody markedly reduced parasite load. This latter effect took place even in T-cell-depleted mice and was accompanied by induction of macrophage toxoplasmacidal activity. CD40 stimulation restricted T. gondii replication independently of STAT1, p47 GTPases, and nitric oxide. In vivo CD40 ligation enhanced tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) production by T. gondii-infected macrophages. In addition, CD40 stimulation required the presence of TNF receptor 2 to reduce parasite load in vivo. These results suggest that CD40-CD154 interaction regulates IFN-gamma-independent mechanisms of host protection through induction of macrophage antimicrobial activity and modulation of TNF-alpha signaling.
Figures
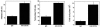
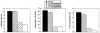


Similar articles
-
CD40 signaling in macrophages induces activity against an intracellular pathogen independently of gamma interferon and reactive nitrogen intermediates.Infect Immun. 2005 May;73(5):3115-23. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.3115-3123.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15845519 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid elimination of Toxoplasma gondii by gamma interferon-primed mouse macrophages is independent of CD40 signaling.Infect Immun. 2007 Oct;75(10):4799-803. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00738-07. Epub 2007 Aug 6. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17682046 Free PMC article.
-
CD154 activates macrophage antimicrobial activity in the absence of IFN-gamma through a TNF-alpha-dependent mechanism.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 15;171(12):6750-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.12.6750. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14662879
-
Cell-mediated immunity to Toxoplasma gondii: initiation, regulation and effector function.Immunobiology. 1999 Dec;201(2):240-7. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(99)80064-3. Immunobiology. 1999. PMID: 10631573 Review.
-
The role of macrophages in protective and pathological responses to Toxoplasma gondii.Parasite Immunol. 2020 Jul;42(7):e12712. doi: 10.1111/pim.12712. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Parasite Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32187690 Review.
Cited by
-
STAT1 Signaling in Astrocytes Is Essential for Control of Infection in the Central Nervous System.mBio. 2016 Nov 8;7(6):e01881-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01881-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27834206 Free PMC article.
-
CD40 and the immune response to parasitic infections.Semin Immunol. 2009 Oct;21(5):273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jul 18. Semin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19616968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD40-CD40L interaction in immunity against protozoan infections.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2007;2007(3):59430. doi: 10.1155/2007/59430. Epub 2007 Apr 10. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17541468 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay of Host Autophagy and Eukaryotic Pathogens.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Sep 13;6:118. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00118. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 30271774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune response and immunopathology during toxoplasmosis.Semin Immunopathol. 2012 Nov;34(6):793-813. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0339-3. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Semin Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 22955326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrade, R. M., M. Wessendarp, J.-A. C. Portillo, J.-Q. Yang, F. J. Gomez, J. E. Durbin, G. A. Bishop, and C. S. Subauste. 2005. TRAF6 signaling downstream of CD40 primes macrophages to acquire anti-microbial activity in response to TNF-α. J. Immunol. 175:6014-6021. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, R. M., M. Wessendarp, and C. S. Subauste. 2003. CD154 activates macrophage anti-microbial activity in the absence of IFN-γ through a TNF-α-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 171:6750-6756. - PubMed
-
- Beaman, M. H., F. G. Araujo, and J. S. Remington. 1994. Protective reconstitution of the SCID mouse against reactivation of toxoplasmic encephalitis. J. Infect. Dis. 169:375-383. - PubMed
-
- Butcher, B. A., L. Kim, P. F. Johnson, and E. Y. Denkers. 2001. Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites inhibit proinflammatory cytokine induction in infected macrophages by preventing nuclear translocation of the transcription factor NFκB. J. Immunol. 167:2193-2201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

