Salmonella enterica highly expressed genes are disease specific
- PMID: 16495536
- PMCID: PMC1418657
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1649-1660.2006
Salmonella enterica highly expressed genes are disease specific
Abstract
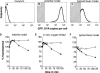
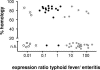
During in vitro broth culture, bacterial gene expression is typically dominated by highly expressed factors involved in protein biosynthesis, maturation, and folding, but it is unclear if this also applies to conditions in natural environments. Here, we used a promoter trap strategy with an unstable green fluorescent protein reporter that can be detected in infected mouse tissues to identify 21 Salmonella enterica promoters with high levels of activity in a mouse enteritis model. We then measured the activities of these and 31 previously identified Salmonella promoters in both the enteritis and a murine typhoid fever model. Surprisingly, the data reveal that instead of protein biosynthesis genes, disease-specific genes such as Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1)-associated genes and genes involved in anaerobic respiration (enteritis) or SPI-2-associated genes and genes of the PhoP regulon (typhoid fever), respectively, dominate Salmonella in vivo gene expression. The overall functional profile of highly expressed genes suggests a marked shift in major transcriptional activities to nutrient utilization during enteritis or to fighting against the host during typhoid fever. The large proportion of known and novel essential virulence factors among the identified genes suggests that high expression levels during infection may correlate with functional relevance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The PhoP/PhoQ system controls the intramacrophage type three secretion system of Salmonella enterica.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jul;57(1):85-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04668.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15948951
-
SseL is a salmonella-specific translocated effector integrated into the SsrB-controlled salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system.Infect Immun. 2007 Feb;75(2):574-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00985-06. Epub 2006 Dec 11. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17158898 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella pathogenicity islands in host specificity, host pathogen-interactions and antibiotics resistance of Salmonella enterica.Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2007 Jul-Aug;120(7-8):317-27. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2007. PMID: 17715824 Review.
-
Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 is expressed prior to penetrating the intestine.PLoS Pathog. 2005 Nov;1(3):e32. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0010032. Epub 2005 Nov 18. PLoS Pathog. 2005. PMID: 16304611 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic modification of microtubule-dependent transport by effector proteins of intracellular Salmonella enterica.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;90(11):897-902. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21803443 Review.
Cited by
-
May Sulfonamide Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrases from Mammaliicoccus sciuri Prevent Antimicrobial Resistance Due to Gene Transfer to Other Harmful Staphylococci?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13827. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213827. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430304 Free PMC article.
-
Riboflavin as a promising antimicrobial agent? A multi-perspective review.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2022 Feb 10;3:100111. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2022.100111. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2022. PMID: 35199072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transduction pathway mediated by the novel regulator LoiA for low oxygen tension induced Salmonella Typhimurium invasion.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jun 2;13(6):e1006429. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006429. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28575106 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of AmyA, an extracellular alpha-glucan degrading enzyme, to group A streptococcal host-pathogen interaction.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Oct;74(1):159-174. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06858.x. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19735442 Free PMC article.
-
The Landscape of Realized Homologous Recombination in Pathogenic Bacteria.Mol Biol Evol. 2016 Feb;33(2):456-71. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv237. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Mol Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 26516092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barthel, M., S. Hapfelmeier, L. Quintanilla-Martinez, M. Kremer, M. Rohde, M. Hogardt, K. Pfeffer, H. Russmann, and W. D. Hardt. 2003. Pretreatment of mice with streptomycin provides a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis model that allows analysis of both pathogen and host. Infect. Immun. 71:2839-2858. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benedik, M. J., and U. Strych. 1998. Serratia marcescens and its extracellular nuclease. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 165:1-13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

