Enrichment and analysis of RNA centered on ion pair reverse phase methodology
- PMID: 16497659
- PMCID: PMC1421089
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2278606
Enrichment and analysis of RNA centered on ion pair reverse phase methodology
Abstract
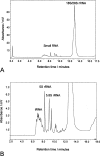
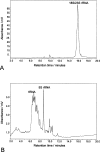
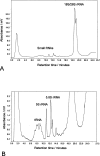
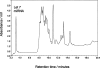
Here we describe a procedure for the rapid enrichment of RNA from cell extracts and the subsequent fractionation and analysis of the "small RNA" population by ion pair reverse phase chromatography. Solid phase extraction procedures have been developed utilizing nonporous alkylated poly(styrene-divinylbenzene) particles in conjunction with ion pair reagents to enrich total RNA. This approach facilitates the selective enrichment and separation of the relatively lower abundance small RNAs, from the more abundant higher molecular weight rRNA species. We also describe the application of monolithic capillaries in conjunction with ion pair reverse phase chromatography to bring increased sensitivity in the analysis of very low abundance RNAs. These approaches will simplify the biochemical analysis of this class of molecules, which are emerging as important regulators of global gene expression in higher organisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of sequence and structure in the separation of nucleic acids using ion pair reverse phase liquid chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 2005 May 27;1076(1-2):83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2005.04.018. J Chromatogr A. 2005. PMID: 15974072
-
High-resolution liquid chromatography of oligonucleotides on nonporous alkylated styrene-divinylbenzene copolymers.Anal Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;212(2):351-8. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1340. Anal Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8214576
-
Reversed-phase ion-pair liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for separation, sequencing and mapping of sites of base modification of isomeric oligonucleotide adducts using monolithic column.J Chromatogr A. 2012 Jul 6;1245:65-74. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 May 9. J Chromatogr A. 2012. PMID: 22652552 Free PMC article.
-
A decade of high-resolution liquid chromatography of nucleic acids on styrene-divinylbenzene copolymers.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002 Dec 25;782(1-2):27-55. doi: 10.1016/s1570-0232(02)00700-6. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 12457994 Review.
-
A guide to large-scale RNA sample preparation.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 May;410(14):3239-3252. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-0943-8. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29546546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterisation and analysis of mRNA critical quality attributes using liquid chromatography based methods.J Chromatogr A. 2025 Mar 29;1745:465724. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2025.465724. Epub 2025 Jan 28. J Chromatogr A. 2025. PMID: 39946818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High resolution fingerprinting of single and double-stranded RNA using ion-pair reverse-phase chromatography.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019 Jan 1;1104:212-219. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.11.027. Epub 2018 Nov 28. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30530113 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro reconstitution of Cascade-mediated CRISPR immunity in Streptococcus thermophilus.EMBO J. 2013 Feb 6;32(3):385-94. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.352. Epub 2013 Jan 18. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23334296 Free PMC article.
-
Ion-Pairing with Triethylammonium Acetate Improves Solid-Phase Extraction of ADP-Ribosylated Peptides.J Proteome Res. 2020 Feb 7;19(2):984-990. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00696. Epub 2020 Jan 7. J Proteome Res. 2020. PMID: 31859514 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterisation of dsRNA using ion pair reverse phase chromatography and mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2017 Feb 10;1484:14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.062. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Chromatogr A. 2017. PMID: 28088361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros, V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431: 350–355. - PubMed
-
- Azarani, A. and Hecker, K.H. 2001. RNA analysis by ion-pair reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 29: e7. http://nar.oupjournals.org. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailey, J.M. and Davidson, N. 1976. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 70: 75–85. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, D.P. 2004. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
