Matrix metalloproteinases in cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 16498509
- PMCID: PMC2780831
- DOI: 10.1016/s0828-282x(06)70983-7
Matrix metalloproteinases in cardiovascular disease
Abstract
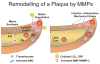
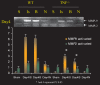
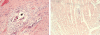
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of proteolytic enzymes that are regulated by inflammatory signals to mediate changes in extracellular matrix. Members of the MMP family share sequence homology, act on interstitial protein substrates, acutely participate in inflammatory processes and chronically mediate tissue remodelling. MMPs are important in vascular remodelling, not only in the overall vasculature architecture but also, more importantly, in the advancing atherosclerotic plaque. MMP activation modifies the architecture of the plaque and may directly participate in the process of plaque rupture. MMPs also participate in cardiac remodelling following myocardial infarction and development of dilated cardiomyopathy. Soluble MMPs are now potential biomarkers in delineating cardiovascular risk for plaque rupture and coronary risk. They also constitute innovative direct or indirect targets to modify cardiovascular tissue remodelling in atherosclerosis and heart failure.
Les métalloprotéinases matricielles (MPM) forment une famille d’enzymes protéolytiques dont la régulation est assurée par des signaux inflammatoires qui amènent des changements au niveau de la matrice extracellulaire. Les membres de la famille des MPM partagent une homologie séquentielle, agissent sur les substrats des protéines interstitielles, participent intensément aux processus inflammatoires et influent à plus long terme sur le remodelage tissulaire. Les MPM sont importantes dans le remodelage des vaisseaux, car elles affectent non seulement leur architecture globale, mais également et surtout, la progression de la plaque d’athérome. L’activation des MPM modifie l’architecture de la plaque et peut participer directement à sa rupture. Les MPM sont en outre impliquées dans le remodelage cardiaque après un infarctus du myocarde et dans le développement de la myocardiopathie dilatée. Les MPM solubles sont désormais des biomarqueurs potentiels qui permettent d’identifier le risque cardiovasculaire associé à la rupture de la plaque et le risque coronarien. Elles constituent en outre de nouvelles cibles directes ou indirectes pour modifier le remodelage du tissu cardiovasculaire en présence d’athérosclérose et d’insuffisance cardiaque.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinases: their biological functions and clinical implications.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2005;106(3):127-32. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2005. PMID: 16026148 Review.
-
Novel therapeutic approaches targeting matrix metalloproteinases in cardiovascular disease.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(10):1214-21. doi: 10.2174/1568026611208011214. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22519451 Review.
-
[Matrix metalloproteinases and atherosclerosis].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2011 Jan 25;65:16-27. doi: 10.5604/17322693.931536. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2011. PMID: 21357991 Review. Polish.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition after myocardial infarction: a new approach to prevent heart failure?Circ Res. 2001 Aug 3;89(3):201-10. doi: 10.1161/hh1501.094396. Circ Res. 2001. PMID: 11485970 Review.
-
Extracellular degradative pathways in myocardial remodeling and progression to heart failure.J Card Fail. 2002 Dec;8(6 Suppl):S332-8. doi: 10.1054/jcaf.2002.129259. J Card Fail. 2002. PMID: 12555141
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Cryopreserved, Allogeneic Extracellular Vesicles for Treatment of Acute Myocardial Infarction.Int Heart J. 2021 Mar 30;62(2):381-389. doi: 10.1536/ihj.20-224. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Int Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33731514 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effects of Aging on the Aorta Stiffness in Relation with Mineral and Trace Element Levels: an Optimized Method via Custom-Built Stretcher Device.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Jul;199(7):2644-2652. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02380-9. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32918713
-
Macrophage maturation from blood monocytes is altered in people with HIV, and is linked to serum lipid profiles and activation indices: A model for studying atherogenic mechanisms.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Oct 1;16(10):e1008869. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008869. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33002093 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-induced left ventricular fibrosis is partially mediated by tumor necrosis factor-α.Physiol Rep. 2021 Nov;9(21):e15062. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15062. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34713972 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac remodeling secondary to chronic volume overload is attenuated by a novel MMP9/2 blocking antibody.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0231202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231202. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32271823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woessner JF., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991;5:2145–54. - PubMed
-
- Massova I, Kotra LP, Fridman R, Mobashery S. Matrix metalloproteinases: Structures, evolution, and diversification. FASEB J. 1998;12:1075–95. - PubMed
-
- Spinale FG, Coker ML, Heung LJ, et al. A matrix metalloproteinase induction/activation system exists in the human left ventricular myocardium and is upregulated in heart failure. Circulation. 2000;102:1944–9. - PubMed
-
- Stewart JA, Jr, Wei CC, Brower GL, et al. Cardiac mast cell- and chymase-mediated matrix metalloproteinase activity and left ventricular remodeling in mitral regurgitation in the dog. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35:311–9. - PubMed
-
- Heymans S, Luttun A, Nuyens D, et al. Inhibition of plasminogen activators or matrix metalloproteinases prevents cardiac rupture but impairs therapeutic angiogenesis and causes cardiac failure. Nat Med. 1999;5:1135–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

