Acute lung infections in normal and immunocompromised hosts
- PMID: 16500210
- PMCID: PMC7119122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rcl.2005.10.009
Acute lung infections in normal and immunocompromised hosts
Abstract
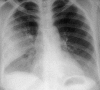
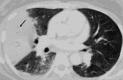
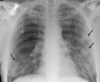
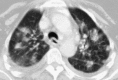
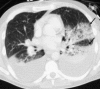
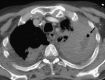
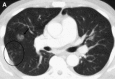
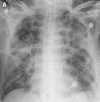
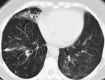
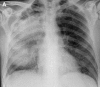
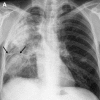
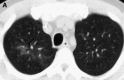
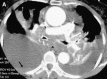
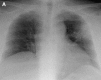
Pulmonary infections are among the most common causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and contribute substantially to annual medical expenditures in the United States. Despite the availability of antimicrobial agents, pneumonia constitutes the sixth most common cause of death and the number one cause of death from infection. Pneumonia can be particularly life-threatening in the elderly, in individuals who have pre-existing heart and lung conditions, in patients who have suppressed or weakened immunity, and in pregnant women. This article discusses some of the important causes of acute lung infections in normal and immunocompromised hosts. Because there often is considerable overlap, infections are categorized by the host immune status that is most likely to be associated with a particular pathogen.
Figures


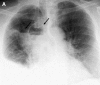



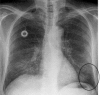
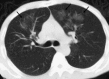
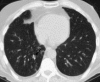
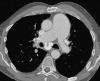
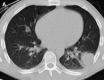

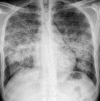
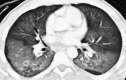
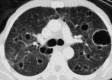
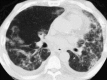
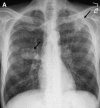

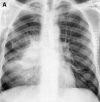

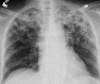

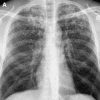


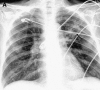

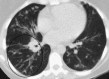






References
-
- Reittner P., Ward S., Heyneman L. Pneumonia: high-resolution CT findings in 114 patients. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(3):515–521. - PubMed
-
- Webb W.R., Higgins C.B. Thoracic imaging-pulmonary and cardiovascular radiology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkens; Philadelphia: 2005.
-
- American Thoracic Society Guidelines for the initial management of adults with community acquired pneumonia: diagnosis, assessment of severity, and initial antimicrobial therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1730–1754. - PubMed
-
- National Center for Health Statistics National hospital discharge survey: annual summary 1990. Vital Health Stat. 1998;13:1–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

