Kruppel-like factor 5 is an important mediator for lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory response in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 16500892
- PMCID: PMC1383625
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl014
Kruppel-like factor 5 is an important mediator for lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory response in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
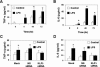
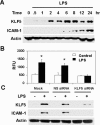
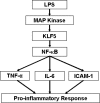
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a bacterially-derived endotoxin that elicits a strong proinflammatory response in intestinal epithelial cells. It is well established that LPS activates this response through NF-kappaB. In addition, LPS signals through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. We previously demonstrated that the Krüppel-like factor 5 [KLF5; also known as intestine-enriched Krüppel-like factor (IKLF)] is activated by the MAPK. In the current study, we examined whether KLF5 mediates the signaling cascade elicited by LPS. Treatment of the intestinal epithelial cell line, IEC6, with LPS resulted in a dose- and time-dependent increase in KLF5 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels. Concurrently, mRNA levels of the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappaB were increased by LPS treatment. Pretreatment with the MAPK inhibitor, U0126, or the LPS antagonist, polymyxin B, resulted in an attenuation of KLF5, p50 and p65 NF-kappaB subunit mRNA levels from LPS treatment. Importantly, suppression of KLF5 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) resulted in a reduction in p50 and p65 subunit mRNA levels and NF-kappaB DNA binding activity in response to LPS. LPS treatment also led to an increase in secretion of TNF-alpha and IL-6 from IEC6, both of which were reduced by siRNA inhibition of KLF5. In addition, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) levels were increased in LPS-treated IEC6 cells and this increase was associated with increased adhesion of Jurkat lymphocytes to IEC6. The induction of ICAM-1 expression and T cell adhesion to IEC6 by LPS were both abrogated by siRNA inhibition of KLF5. These results indicate that KLF5 is an important mediator for the proinflammatory response elicited by LPS in intestinal epithelial cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Perfluorocarbon attenuates lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory responses of alveolar epithelial cells in vitro.Chin Med J (Engl). 2011 Aug;124(16):2534-9. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011. PMID: 21933601
-
Bcl10 mediates LPS-induced activation of NF-kappaB and IL-8 in human intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):G429-37. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00149.2007. Epub 2007 May 31. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17540779
-
Krüppel-like factor 5 mediates proinflammatory cytokine expression in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through upregulation of nuclear factor-κB phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:281984. doi: 10.1155/2014/281984. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 25197166 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of the transcription factor KLF5 in cardiovascular remodeling.J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Aug;3(8):1569-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01366.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2005. PMID: 16102021 Review.
-
Essential role of KLF5 transcription factor in cell proliferation and differentiation and its implications for human diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Aug;66(16):2691-706. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0045-z. Epub 2009 May 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19448973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chorioamnionitis-induced fetal gut injury is mediated by direct gut exposure of inflammatory mediators or by lung inflammation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Mar 1;306(5):G382-93. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00260.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24458021 Free PMC article.
-
KLF5 Is Crucial for Androgen-AR Signaling to Transactivate Genes and Promote Cell Proliferation in Prostate Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 21;12(3):748. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030748. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32245249 Free PMC article.
-
Interruption of KLF5 acetylation converts its function from tumor suppressor to tumor promoter in prostate cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2015 Feb 1;136(3):536-46. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29028. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 24931571 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of chlorogenic acid on acute hepatotoxicity induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice.Inflamm Res. 2010 Oct;59(10):871-7. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0199-z. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 20405164
-
Downregulation of Krüppel‑like factor 1 inhibits the metastasis and invasion of cervical cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Oct;18(4):3932-3940. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9401. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30132534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowie A.G., Haga I.R. The role to Toll-like receptors in the host response to viruses. Mol. Immunol. 2005;42:859–867. - PubMed
-
- Rhee S.H., Hwang D. Murine TOLL-like receptor 4 confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness as determined by activation of NF kappa B and expression of the inducible cyclooxygenase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:34035–34040. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K. Evolution and integration of innate immune recognition systems: the Toll-like receptors. J. Endotoxin Res. 2005;11:51–55. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Takeuchi O., Fujita T., Inoue J., Muhlradt P.F., Sato S., Hoshino K., Akira S. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates the MyD88-independent pathway and results in activation of IFN-regulatory factor 3 and the expression of a subset of lipopolysaccharide-inducible genes. J. Immunol. 2001;167:5887–5894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

