Checkpoint functions are required for normal S-phase progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae RCAF- and CAF-I-defective mutants
- PMID: 16501045
- PMCID: PMC1533778
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0511102103
Checkpoint functions are required for normal S-phase progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae RCAF- and CAF-I-defective mutants
Abstract
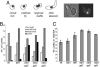
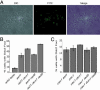
The chromatin-assembly factor I (CAF-I) and the replication-coupling assembly factor (RCAF) complexes function in chromatin assembly during DNA replication and repair and play a role in the maintenance of genome stability. Here, we have investigated their role in checkpoints and S-phase progression. FACS analysis of mutants lacking Asf1 or Cac1 as well as various checkpoint proteins indicated that normal rates of S-phase progression in asf1 mutants have a strong requirement for replication checkpoint proteins, whereas normal S-phase progression in cac1 mutants has only a weak requirement for either replication or DNA-damage checkpoint proteins. Furthermore, asf1 mutants had high levels of Ddc2.GFP foci that were further increased in asf1 dun1 double mutants consistent with a requirement for checkpoint proteins in S-phase progression in asf1 mutants, whereas cac1 mutants had much lower levels of Ddc2.GFP foci that were not increased by a dun1 mutation. Our data suggest that RCAF defects lead to unstable replication forks that are then stabilized by replication checkpoint proteins, whereas CAF-I defects likely cause different types of DNA damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures



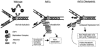
References
-
- Ye X., Franco A. A., Santos H., Nelson D. M., Kaufman P. D., Adams P. D. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:341–351. - PubMed
-
- Loyola A., Almouzni G. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1677:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Smith S., Stillman B. Cell. 1989;58:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Gaillard P. H., Martini E. M., Kaufman P. D., Stillman B., Moustacchi E., Almouzni G. Cell. 1996;86:887–896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

