The rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4 directly interacts with the caveolar structural protein caveolin-1
- PMID: 16501093
- PMCID: PMC1395425
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.6.2842-2854.2006
The rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4 directly interacts with the caveolar structural protein caveolin-1
Abstract
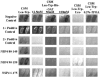
Rotavirus nonstructural protein 4 (NSP4) is known to function as an intracellular receptor at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) critical to viral morphogenesis and is the first characterized viral enterotoxin. Exogenously added NSP4 induces diarrhea in rodent pups and stimulates secretory chloride currents across intestinal segments as measured in Ussing chambers. Circular dichroism studies further reveal that intact NSP4 and the enterotoxic peptide (NSP4(114-135)) that is located within the extended, C-terminal amphipathic helix preferentially interact with caveola-like model membranes. We now show colocalization of NSP4 and caveolin-1 in NSP4-transfected and rotavirus-infected mammalian cells in reticular structures surrounding the nucleus (likely ER), in the cytosol, and at the cell periphery by laser scanning confocal microscopy. A direct interaction between NSP4 residues 112 to 140 and caveolin-1 was determined by the Pro-Quest yeast two-hybrid system with full-length NSP4 and seven overlapping deletion mutants as bait, caveolin-1 as prey, and vice versa. Coimmunoprecipitation of NSP4-caveolin-1 complexes from rotavirus-infected mammalian cells demonstrated that the interaction occurs during viral infection. Finally, binding of caveolin-1 from mammalian cell lysates to Sepharose-bound, NSP4-specific synthetic peptides confirmed the yeast two-hybrid data and further delineated the binding domain to amino acids 114 to 135. We propose that the association of NSP4 and caveolin-1 contributes to NSP4 intracellular trafficking from the ER to the cell surface and speculate that exogenously added NSP4 stimulates signaling molecules located in caveola microdomains.
Figures

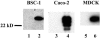






References
-
- Anderson, R. G. W. 1998. The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67:199-225. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 2002. ProQuest two-hybrid system with Gateway Technology manual. Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, Calif.
-
- Ball, J. M., D. M. Mitchell, T. F. Gibbons, and R. D. Parr. 2005. Rotavirus NSP4: a multifunctional viral enterotoxin. Viral Immunol. 18:27-40. - PubMed
-
- Ball, J. M., P. Tian, C. Q. Y. Zeng, A. P. Morris, and M. K. Estes. 1996. Age-dependent diarrhea induced by a rotaviral nonstructural glycoprotein. Science 272:101-104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

