Simian immunodeficiency virus engrafted with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-specific epitopes: replication, neutralization, and survey of HIV-1-positive plasma
- PMID: 16501112
- PMCID: PMC1395451
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.6.3030-3041.2006
Simian immunodeficiency virus engrafted with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-specific epitopes: replication, neutralization, and survey of HIV-1-positive plasma
Abstract
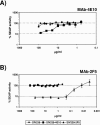
To date, only a small number of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) with relatively broad neutralizing activity have been isolated from infected individuals. Adequate techniques for defining how frequently antibodies of these specificities arise in HIV-infected people have been lacking, although it is generally assumed that such antibodies are rare. In order to create an epitope-specific neutralization assay, we introduced well-characterized HIV-1 epitopes into the heterologous context of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). Specifically, epitope recognition sequences for the 2F5, 4E10, and 447-52D anti-HIV-1 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies were introduced into the corresponding regions of SIVmac239 by site-directed mutagenesis. Variants with 2F5 or 4E10 recognition sequences in gp41 retained replication competence and were used for neutralization assays. The parental SIVmac239 and the neutralization-sensitive SIVmac316 were not neutralized by the 2F5 and 4E10 MAbs, nor were they neutralized significantly by any of the 96 HIV-1-positive human plasma samples that were tested. The SIV239-2F5 and SIV239-4E10 variants were specifically neutralized by the 2F5 and 4E10 MAbs, respectively, at concentrations within the range of what has been reported previously for HIV-1 primary isolates (J. M. Binley et al., J. Virol. 78:13232-13252, 2004). The SIV239-2F5 and SIV239-4E10 epitope-engrafted variants were used as biological screens for the presence of neutralizing activity of these specificities. None of the 92 HIV-1-positive human plasma samples that were tested exhibited significant neutralization of SIV239-2F5. One plasma sample exhibited >90% neutralization of SIV239-4E10, but this activity was not competed by a 4E10 target peptide and was not present in concentrated immunoglobulin G (IgG) or IgA fractions. We thus confirm by direct analysis that neutralizing activities of the 2F5 and 4E10 specificities are either rare among HIV-1-positive individuals or, if present, represent only a very small fraction of the total neutralizing activity in any given plasma sample. We further conclude that the structures of gp41 from SIVmac239 and HIV-1 are sufficiently similar such that epitopes engrafted into SIVmac239 can be readily recognized by the cognate anti-HIV-1 monoclonal antibodies.
Figures

References
-
- Barbato, G., E. Bianchi, P. Ingallinella, W. H. Hurni, M. D. Miller, G. Ciliberto, R. Cortese, R. Bazzo, J. W. Shiver, and A. Pessi. 2003. Structural analysis of the epitope of the anti-HIV antibody 2F5 sheds light into its mechanism of neutralization and HIV fusion. J. Mol. Biol. 330:1101-1115. - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., T. Wrin, B. Korber, M. B. Zwick, M. Wang, C. Chappey, G. Stiegler, R. Kunert, S. Zolla-Pazner, H. Katinger, C. J. Petropoulos, and D. R. Burton. 2004. Comprehensive cross-clade neutralization analysis of a panel of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 78:13232-13252. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biron, Z., S. Khare, A. O. Samson, Y. Hayek, F. Naider, and J. Anglister. 2002. A monomeric 3(10)-helix is formed in water by a 13-residue peptide representing the neutralizing determinant of HIV-1 on gp41. Biochemistry 41:12687-12696. - PubMed
-
- Buchacher, A., R. Predl, K. Strutzenberger, W. Steinfellner, A. Trkola, M. Purtscher, G. Gruber, C. Tauer, F. Steindl, A. Jungbauer et al. 1994. Generation of human monoclonal antibodies against HIV-1 proteins; electrofusion and Epstein-Barr virus transformation for peripheral blood lymphocyte immortalization. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 10:359-369. - PubMed
-
- Burton, D. R., E. O. Saphire, and P. W. Parren. 2001. A model for neutralization of viruses based on antibody coating of the virion surface. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 260:109-143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI062524/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 33292/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI058725/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI50421/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI043638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR00168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI 36214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027670/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR000168/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI29164/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050421/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI029164/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27670/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI058725/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI043638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI033292/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033292/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI062524/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

