Collection, storage, preservation, and normalization of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery
- PMID: 16501490
- PMCID: PMC2276656
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000273
Collection, storage, preservation, and normalization of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery
Abstract
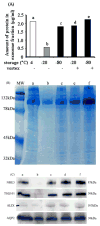
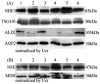
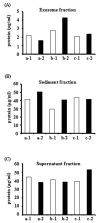
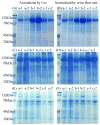
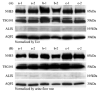
Urinary exosomes containing apical membrane and intracellular fluid are normally secreted into the urine from all nephron segments, and may carry protein markers of renal dysfunction and structural injury. We studied methods for collection, storage, and preservation of urinary exosomal proteins. We collected urine from healthy volunteers, added protease inhibitors, and stored urine samples at 4, -20, and -80 degrees C for 1 week or 7 months. Samples were thawed with and without extensive vortexing, and three fractions were isolated: urinary sediment, supernatant, and exosome fraction. Protein concentration, electrophoresis patterns, and abundance of seven exosome-associated proteins were measured. Exosome-associated proteins were not detected in sediment or supernatant fractions. Protease inhibitors prevented degradation of exosome-associated proteins. Freezing at -20 degrees C caused a major loss in exosomes compared to fresh urine. In contrast, recovery after freezing at -80 degrees C was almost complete. Extensive vortexing after thawing markedly increased exosome recovery in urine frozen at -20 or -80 degrees C, even if frozen for 7 months. The recovery from first and second morning urine was similar. The abundance of cytosolic exosome-associated proteins did not decrease during long-term storage. We concluded: (1) protease inhibitors are essential for preservation; (2) storage at -80 degrees C with extensive vortexing after thawing maximizes the recovery of urinary exosomes; (3) the difference between first and second morning urine exosome-associated protein was small, suggesting minimal protein degradation in the urinary tract/bladder; (4) urinary exosomes remain intact during long-term storage. These urine collection, storage, and processing conditions may be useful for future biomarker discovery efforts.
Figures
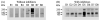
References
-
- Hewitt SM, Dear J, Star RA. Discovery of protein biomarkers for renal diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1677–89. - PubMed
-
- du Cheyron D, Daubin C, Poggioli J, et al. Urinary measurement of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 (NHE3) protein as new marker of tubule injury in critically ill patients with ARF. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:497–506. - PubMed
-
- Hoorn EJ, Pisitkun T, Zietse R, et al. Prospects for urinary proteomics: Exosomes as a source of urinary biomarkers. Nephrology (Carlton) 2005;10:283–90. - PubMed
-
- Thongboonkerd V, Klein E, Klein JB. Sample preparation for 2-D proteomic analysis. Contrib Nephrol. 2004;141:11–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

