Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver treated by hepatic resection: a case report
- PMID: 16502497
- PMCID: PMC2687572
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.140
Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver treated by hepatic resection: a case report
Abstract
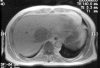
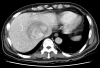
Inflammatory pseudotumor (IPT) of the liver is rare benign tumor. When the diagnosis of IPT is established with biopsy, simple observation or conservative therapy is preferred because of the possibility of regression. But IPT is unresponsive to the conservative treatment, surgical resection should be considered. We experienced a 63-year-old male, who was suspected hepatocellular carcinoma in abdominal computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance image (MRI) scan, presented with 2-month history of intermittent fever and weight loss. Percutaneous ultrasound guided core biopsy confirmed IPT of the liver. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics were administered for 8 and 4 weeks, respectively, but fever continued. So, extended right hepatectomy was performed for IPT of the liver and then fever subsided. The patient remains well during a follow-up period of 12 months.
Figures



References
-
- Broughan TA, Fischer WL, Tuthill RJ. Vascular invasion by hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor. A clinicopathologic study. Cancer. 1993;71:2934–2940. - PubMed
-
- Byun YJ, Chung BH, Kwon KW. Inflammatory pseudotumor of urinary bladder. Yonsei Med J. 2000;41:273–275. - PubMed
-
- Choi SK, Choi YD, Cheon SH, Byun Y, Cho SW. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder in a child. Yonsei Med J. 2000;41:401–403. - PubMed
-
- Torzilli G, Inoue K, Midorikawa Y, Hui AM, Takayama T, Makuuchi M. Inflammatory pseudotumors of the liver: prevalence and clinical impact in surgical patients. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001;48:1118–1123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

