Nidovirales: evolving the largest RNA virus genome
- PMID: 16503362
- PMCID: PMC7114179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2006.01.017
Nidovirales: evolving the largest RNA virus genome
Abstract
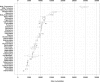
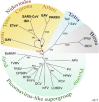
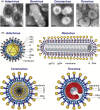
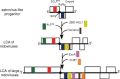
This review focuses on the monophyletic group of animal RNA viruses united in the order Nidovirales. The order includes the distantly related coronaviruses, toroviruses, and roniviruses, which possess the largest known RNA genomes (from 26 to 32kb) and will therefore be called "large" nidoviruses in this review. They are compared with their arterivirus cousins, which also belong to the Nidovirales despite having a much smaller genome (13-16kb). Common and unique features that have been identified for either large or all nidoviruses are outlined. These include the nidovirus genetic plan and genome diversity, the composition of the replicase machinery and virus particles, virus-specific accessory genes, the mechanisms of RNA and protein synthesis, and the origin and evolution of nidoviruses with small and large genomes. Nidoviruses employ single-stranded, polycistronic RNA genomes of positive polarity that direct the synthesis of the subunits of the replicative complex, including the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and helicase. Replicase gene expression is under the principal control of a ribosomal frameshifting signal and a chymotrypsin-like protease, which is assisted by one or more papain-like proteases. A nested set of subgenomic RNAs is synthesized to express the 3'-proximal ORFs that encode most conserved structural proteins and, in some large nidoviruses, also diverse accessory proteins that may promote virus adaptation to specific hosts. The replicase machinery includes a set of RNA-processing enzymes some of which are unique for either all or large nidoviruses. The acquisition of these enzymes may have improved the low fidelity of RNA replication to allow genome expansion and give rise to the ancestors of small and, subsequently, large nidoviruses.
Figures


References
-
- Allen M.D., Buckle A.M., Cordell S.C., Lowe J., Bycroft M. The crystal structure of AF1521 a protein from Archaeoglobus fulgidus with homology to the non-histone domain of MacroH2A. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;330:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Anand K., Ziebuhr J., Wadhwani P., Mesters J.R., Hilgenfeld R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science. 2003;300:1763–1767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

