BIPAD: a web server for modeling bipartite sequence elements
- PMID: 16503993
- PMCID: PMC1388241
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-76
BIPAD: a web server for modeling bipartite sequence elements
Abstract
Background: Many dimeric protein complexes bind cooperatively to families of bipartite nucleic acid sequence elements, which consist of pairs of conserved half-site sequences separated by intervening distances that vary among individual sites.
Results: We introduce the Bipad Server, a web interface to predict sequence elements embedded within unaligned sequences. Either a bipartite model, consisting of a pair of one-block position weight matrices (PWM's) with a gap distribution, or a single PWM matrix for contiguous single block motifs may be produced. The Bipad program performs multiple local alignment by entropy minimization and cyclic refinement using a stochastic greedy search strategy. The best models are refined by maximizing incremental information contents among a set of potential models with varying half site and gap lengths.
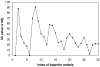
Conclusion: The web service generates information positional weight matrices, identifies binding site motifs, graphically represents the set of discovered elements as a sequence logo, and depicts the gap distribution as a histogram. Server performance was evaluated by generating a collection of bipartite models for distinct DNA binding proteins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bipartite pattern discovery by entropy minimization-based multiple local alignment.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Sep 23;32(17):4979-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh825. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15388800 Free PMC article.
-
SCOPE: a web server for practical de novo motif discovery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W259-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm310. Epub 2007 May 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17485471 Free PMC article.
-
On counting position weight matrix matches in a sequence, with application to discriminative motif finding.Bioinformatics. 2006 Jul 15;22(14):e454-63. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl227. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16873507
-
The relative value of operon predictions.Brief Bioinform. 2008 Sep;9(5):367-75. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbn019. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Brief Bioinform. 2008. PMID: 18420711 Review.
-
Homology assessment and molecular sequence alignment.J Biomed Inform. 2006 Feb;39(1):18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2005.11.005. Epub 2005 Dec 9. J Biomed Inform. 2006. PMID: 16380300 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative transcription cycle for bacterial RNA polymerase.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 23;11(1):448. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14208-9. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31974358 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of ResD, NsrR, and Fur Binding in Bacillus subtilis during Anaerobic Fermentative Growth by In Vivo Footprinting.J Bacteriol. 2017 Jun 13;199(13):e00086-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00086-17. Print 2017 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28439033 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution mapping of in vivo genomic transcription factor binding sites using in situ DNase I footprinting and ChIP-seq.DNA Res. 2013 Aug;20(4):325-38. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dst013. Epub 2013 Apr 11. DNA Res. 2013. PMID: 23580539 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and evolution of control logic in prokaryotic transcriptional regulation.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Sep;73(3):481-509, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00037-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19721087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Streptomyces filipinensis Gamma-Butyrolactone System Reveals Novel Clues for Understanding the Control of Secondary Metabolism.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Sep 1;86(18):e00443-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00443-20. Print 2020 Sep 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32631864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bi CP, Rogan PK. Bipad. 2004. http://bipad.cmh.edu
-
- Claessens F, Gerwith D. DNA recognition by nuclear receptors. Essays in Biochemistry. 2004;40:59–72. - PubMed
-
- Aranda A, Pasucal A. Nuclear hormone receptors and gene expression. Physiological Reviews. 2001;81:1269–1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

