Proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma modulate epithelial barrier function in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells through mitogen activated protein kinase signaling
- PMID: 16504032
- PMCID: PMC1402323
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6793-6-2
Proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma modulate epithelial barrier function in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells through mitogen activated protein kinase signaling
Abstract
Background: The tight junction is a dynamic structure that is regulated by a number of cellular signaling processes. Occludin, claudin-1, claudin-2 and claudin-3 are integral membrane proteins found in the tight junction of MDCK cells. These proteins are restricted to this region of the membrane by a complex array of intracellular proteins which are tethered to the cytoskeleton. Alteration of these tight junction protein complexes during pathological events leads to impaired epithelial barrier function that perturbs water and electrolyte homeostasis. We examined MDCK cell barrier function in response to challenge by the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) and interferon-gamma (IFNgamma).
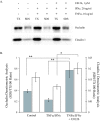
Results: Exposure of MDCK cells to TNFalpha/IFNgamma resulted in a marked sustained elevation of transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) as well as elevated paracellular permeability. We demonstrate that the combination of TNFalpha/IFNgamma at doses used in this study do not significantly induce MDCK cell apoptosis. We observed significant alterations in occludin, claudin-1 and claudin-2 protein expression, junctional localization and substantial cytoskeletal reorganization. Pharmacological inhibition of ERK1/2 and p38 signaling blocked the deleterious effects of the proinflammatory cytokines on barrier function.
Conclusion: These data strongly suggest that downstream effectors of MAP kinase signaling pathways mediate the TNFalpha/IFNgamma-induced junctional reorganization that modulates MDCK cell barrier function.
Figures

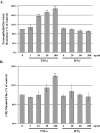

 ), TNFα/IFNγ, 3/6 ng/ml (
), TNFα/IFNγ, 3/6 ng/ml ( ), TNFα/IFNγ, 10/20 ng/ml (
), TNFα/IFNγ, 10/20 ng/ml ( ), and TNFα/IFNγ, 30/60 ng/ml (
), and TNFα/IFNγ, 30/60 ng/ml ( ). Panel B reports the mean [3H]-mannitol flux following 72 hour incubation with the indicated treatments. Flux is presented as the percent of apical [3H]-mannitol recovered in the basolateral chamber following 120 min. incubation. Error bars represent the SE, n = 6. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed, multiple comparisons between control and treatments were determined with the Bonferroni post test. **Indicates statistical difference (P < 0.001) to control.
). Panel B reports the mean [3H]-mannitol flux following 72 hour incubation with the indicated treatments. Flux is presented as the percent of apical [3H]-mannitol recovered in the basolateral chamber following 120 min. incubation. Error bars represent the SE, n = 6. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed, multiple comparisons between control and treatments were determined with the Bonferroni post test. **Indicates statistical difference (P < 0.001) to control.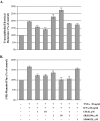


References
-
- Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:G467–75. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Padura I, Lostaglio S, Schneemann M, Williams L, Romano M, Fruscella P, Panzeri C, Stoppacciaro A, Ruco L, Villa A, Simmons D, Dejana E. Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. J Cell Biol. 1998;142:117–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mitic LL, Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions I. Tight junction structure and function: lessons from mutant animals and proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G250–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

