Using individual growth model to analyze the change in quality of life from adolescence to adulthood
- PMID: 16504035
- PMCID: PMC1397823
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-4-10
Using individual growth model to analyze the change in quality of life from adolescence to adulthood
Abstract
Background: The individual growth model is a relatively new statistical technique now widely used to examine the unique trajectories of individuals and groups in repeated measures data. This technique is increasingly used to analyze the changes over time in quality of life (QOL) data. This study examines the change from adolescence to adulthood in physical health as an aspect of QOL as an illustration of the use of this analytic method.
Methods: Employing data from the Children in the Community (CIC) study, a prospective longitudinal investigation, physical health was assessed at mean ages 16, 22, and 33 in 752 persons born between 1965 and 1975.
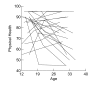
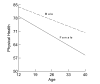
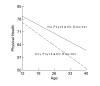
Results: The analyses using individual growth models show a linear decline in average physical health from age 10 to age 40. Males reported better physical health and declined less per year on average. Time-varying psychiatric disorders accounted for 8.6% of the explained variation in mean physical health, and 6.7% of the explained variation in linear change in physical health. Those with such a disorder reported lower mean physical health and a more rapid decline with age than those without a current psychiatric disorder. The use of SAS PROC MIXED, including syntax and interpretation of output are provided. Applications of these models including statistical assumptions, centering issues and cohort effects are discussed.
Conclusion: This paper highlights the usefulness of the individual growth model in modeling longitudinal change in QOL variables.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of adolescent mental disorders and physical illnesses on quality of life 17 years later.Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006 Jan;160(1):93-9. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.160.1.93. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006. PMID: 16389217
-
CDC National Health Report: leading causes of morbidity and mortality and associated behavioral risk and protective factors--United States, 2005-2013.MMWR Suppl. 2014 Oct 31;63(4):3-27. MMWR Suppl. 2014. PMID: 25356673
-
Examining changes in self-perceived quality of life in children and adolescents with physical disability using a longitudinal design.Disabil Rehabil. 2011;33(19-20):1873-9. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2011.552664. Epub 2011 Feb 10. Disabil Rehabil. 2011. PMID: 21309649
-
Mindfulness and bodily distress.Dan Med J. 2012 Nov;59(11):B4547. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 23171754 Review.
-
A comparison of three approaches for identifying correlates of heterogeneity in change.New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2021 Jan;2021(175):141-160. doi: 10.1002/cad.20390. Epub 2021 Jan 17. New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2021. PMID: 33458943 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal beta regression models for analyzing health-related quality of life scores over time.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012 Sep 17;12:144. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-144. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012. PMID: 22984825 Free PMC article.
-
Urgent engagement in 9/11 pregnant widows and their infants: Transmission of trauma.Infancy. 2020 Mar;25(2):165-189. doi: 10.1111/infa.12323. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Infancy. 2020. PMID: 32749044 Free PMC article.
-
The origins of 12-month attachment: a microanalysis of 4-month mother-infant interaction.Attach Hum Dev. 2010 Jan;12(1-2):3-141. doi: 10.1080/14616730903338985. Attach Hum Dev. 2010. PMID: 20390524 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Quality of Life for Parents of Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.J Pediatr. 2024 Jan;264:113773. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2023.113773. Epub 2023 Oct 13. J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 37839508 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of driving cessation on health-related quality of life trajectories.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2024 Feb 1;22(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12955-024-02231-4. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2024. PMID: 38302929 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous