Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins in human cervical cancer
- PMID: 16504151
- PMCID: PMC1403791
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-45
Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins in human cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: It has been shown that IAPs, in particular XIAP, survivin and c-IAP1, are overexpressed in several malignancies. In the present study we investigate the expression of c-IAP1, c-IAP2, XIAP and survivin and its isoforms in cervical cancer.
Methods: We used semiquantitative RT-PCR assays to analyze 41 cancer and 6 normal tissues. The study included 8 stage I cases; 16 stage II; 17 stageIII; and a control group of 6 samples of normal cervical squamous epithelial tissue.
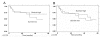
Results: c-IAP2 and XIAP mRNA levels were similar among the samples, cervical tumors had lower c-IAP1 mRNA levels. Unexpectedly, a clear positive association was found between low levels of XIAP and disease relapse. A log-rank test showed a significant inverse association (p = 0.02) between XIAP expression and tumor aggressiveness, as indicated by disease relapse rates. There were no statistically significant differences in the presence or expression levels of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 among any of the clinical variables studied. Survivin and its isoforms were undetectable in normal cervical tissues, in contrast with the clear upregulation observed in cancer samples. We found no association between survivin expression and age, clinical stage, histology or menopausal state. Nevertheless, we found that adenocarcinoma tumors expressed higher levels of survivin 2B and DeltaEx3 (p = 0.001 and p = 0.04 respectively, by Kruskal-Wallis). A multivariate Cox's partial likelihood-based analysis showed that only FIGO stage was an independent predictor of outcome.
Conclusion: There are no differences in the expression of c-IAP2 and XIAP between normal vs. cancer samples, but XIAP expression correlate in cervical cancer with relapse of this disease in the patients. Otherwise, c-IAP1 was downregulated in the cervical cancer samples. The expression of survivin was upregulated in the patients with cervical cancer. We have found that adenocarcinoma presented higher levels of survivin isoforms 2B and DeltaEx3.
Figures


References
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins--suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:239–252. - PubMed

