High predictive value of epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation but not of EGFRvIII mutation in resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- PMID: 16505275
- PMCID: PMC1860345
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2005.027615
High predictive value of epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation but not of EGFRvIII mutation in resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Abstract
Aims: Overexpression and mutation of epidermal growth factor regulator (EGFR) are frequently found in the carcinogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Because targeting of this receptor has proven therapeutic efficacy, studying EGFR has become a matter of particular scientific interest. The present study analysed the EGFR receptor, rate of EGFRvIII mutations, and rate of activated phosphorylated EGFR (pEGFR) by immunohistochemistry on cryostat sections.
Methods: Surgically obtained tumour specimens of a series of 78 NSCLC patients and 66 adjacent tumour free specimens were examined immunohistochemically using monoclonal antibodies to stain EGFR, pEGFR, and EGFRvIII.
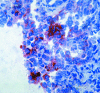
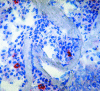
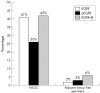
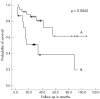
Results: EGFRvIII and pEGFR expression was found in 42% and 26% of the tumours respectively and both were increased significantly compared with tumour free samples. EGFR, pEGFR, and EGFRvIII expression did not correlate with any of the previously tested markers (c-erbB-2, c-erbB-3, p53, ki-67, and microvessel density). Similar distributions of immunohistochemical profiles were seen, regardless of histological subtype, age, or sex. In stage I patients, EGFR phosphorylation at tyrosine residue 845 proved to be an independent prognostic factor.
Conclusion: Because pEGFR correlated with poor prognosis, it can be speculated that it plays a crucial biological role in the pathogenesis of NSCLC.
Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and p-EGFR expression in resected non-small cell lung cancer.Exp Lung Res. 2010 Nov;36(9):531-7. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2010.482176. Exp Lung Res. 2010. PMID: 20939760
-
Activated epidermal growth factor receptor-Stat-3 signaling promotes tumor survival in vivo in non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 1;11(23):8288-94. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0827. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16322287
-
Influence of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutations on the expression of EGFR, phosphoryl-Akt, and phosphoryl-MAPK, and on the prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2007 Jan 1;95(1):63-9. doi: 10.1002/jso.20547. J Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17192868
-
Immunohistochemical markers of prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer: a review and proposal for a multiphase approach to marker evaluation.J Clin Pathol. 2006 Aug;59(8):790-800. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.031351. J Clin Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16873561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Molecular diagnostics of epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer].Lege Artis Med. 2007 Oct;17(10):681-7. Lege Artis Med. 2007. PMID: 19227598 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
GBM heterogeneity as a function of variable epidermal growth factor receptor variant III activity.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79101-79116. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12600. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27738329 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Co-Expression Rate of HER2 and HER3 Biomarkers in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Sep 1;25(9):2979-2990. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.9.2979. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39342574 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EGF-receptor-signalling in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck.Br J Cancer. 2007 Feb 12;96(3):408-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603566. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17224925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Design of a Dephosphorylation-Resistant Reporter Enables Single-Cell Measurement of Tyrosine Kinase Activity.ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):355-62. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00667. Epub 2015 Dec 4. ACS Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26587880 Free PMC article.
-
Activated epidermal growth factor receptor in ovarian cancer.Cancer Treat Res. 2009;149:203-26. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-98094-2_10. Cancer Treat Res. 2009. PMID: 19763438 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Parkin D M. Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol 20012533–543. - PubMed
-
- Dy G K, Adjei A A. Novel targets for lung cancer therapy: part I. J Clin Oncol 2002202881–2894. - PubMed
-
- Kris M G, Azzoli C G, Miller V A. Epidermal growth factor receptor blockade: targeted therapy for non‐small‐cell lung cancer. In: ASCO Educational Book. Alexandria, USA: ASCO, 2002693–699.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous