Retinoic acid is required early during adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus
- PMID: 16505366
- PMCID: PMC1450163
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0511294103
Retinoic acid is required early during adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus
Abstract
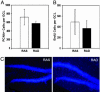
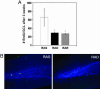
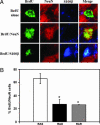
Retinoic acid (RA) is commonly used in vitro to differentiate stem cell populations including adult neural stem cells into neurons; however, the in vivo function of RA during adult neurogenesis remains largely unexplored. We found that depletion of RA in adult mice leads to significantly decreased neuronal differentiation within the granular cell layer of the dentate gyrus. RA contribution to neurogenesis occurs early, for RA deficiency also results in a decrease in newborn cells expressing an immature neuronal marker. Furthermore, although proliferation is unaffected during RA absence, cell survival is significantly reduced. Finally, a screen for retinoid-induced genes identifies metabolic targets including the lipid transporters, CD-36 and ABCA-1, the lipogenic master regulator SREBP1c as well as components of the Wnt signaling pathway. Our results reveal RA as a crucial contributor to early stages of adult neurogenesis and survival in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
References
-
- Maden M. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002;3:843–853. - PubMed
-
- Durston A. J., Timmermans J. P., Hage W. J., Hendriks H. F., de Vries N. J., Heideveld M., Nieuwkoop P. D. Nature. 1989;340:140–144. - PubMed
-
- Pierani A., Brenner-Morton S., Chiang C., Jessell T. M. Cell. 1999;97:903–915. - PubMed
-
- Beato M., Herrlich P., Schutz G. Cell. 1995;83:851–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

