Hepatitis C: a review for primary care physicians
- PMID: 16505462
- PMCID: PMC1389829
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.1030034
Hepatitis C: a review for primary care physicians
Erratum in
- CMAJ. 2006 May 9;174(10):1450
Abstract
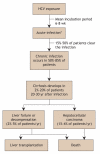
Primary care physicians see many of the estimated 250 000 Canadians chronically infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Of this number, about one-third are unaware they are infected, which constitutes a large hidden epidemic. They continue to spread HCV unknowingly and cannot benefit from advances in antiviral therapy that may clear them of the virus. Many HCV-infected people remain asymptomatic, which means it is important to assess for risk factors and test patients accordingly. The third-generation enzyme immunoassay for HCV antibodies is a sensitive and specific test, although the presence of the virus can be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction testing for HCV RNA in some circumstances. Pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin combination therapy clears the virus in about 45%-80% of patients, depending on viral genotype. Preventive strategies and counselling recommendations are also reviewed.
Figures



Comment in
-
Hepatitis C: reviewing the options.CMAJ. 2006 Jul 4;175(1):63-4; author reply 64. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1060092. CMAJ. 2006. PMID: 16818917 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hepatitis C: reviewing the options.CMAJ. 2006 Jul 4;175(1):63; author reply 64. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1060100. CMAJ. 2006. PMID: 16818918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, et al. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science 1989;244:359-62. - PubMed
-
- Murphy DG, Willems B, Delage G, et al. Hepatitis C virus genotypes in patients and blood donors — Quebec. Can Commun Dis Rep 1995;21:129-32. - PubMed
-
- Shepard CW, Finelli L, Alter MJ. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis 2005;5:558-67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
