Localization of soluble guanylyl cyclase in the superficial dorsal horn
- PMID: 16506200
- PMCID: PMC2597089
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.20901
Localization of soluble guanylyl cyclase in the superficial dorsal horn
Abstract
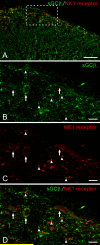
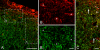
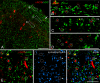
Nitric oxide (NO) has been implicated in pain processing at the spinal level, but the mechanisms mediating its effects remain unclear. In the present work, we studied the organization of the major downstream effector of NO, soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC), in the superficial dorsal horn of rat. Almost all neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor-positive neurons in lamina I (a major source of ascending projections) were strongly immunopositive for sGC. Many local circuit neurons in laminae I-II also stained for sGC, but less intensely. Numerous fibers, presumably of unmyelinated primary afferent (C fiber) origin, stained for calcitonin gene-related peptide or isolectin B4, but none of these was immunopositive for sGC. These data, along with immunoelectron microscopy results, imply that unmyelinated primary afferent fibers terminating in the superficial dorsal horn lack sGC. Double labeling showed that neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) seldom colocalized with sGC, but nNOS-positive structures were frequently closely apposed to sGC-positive structures, suggesting that in the superficial dorsal horn NO acts mainly in a paracrine manner. Our data suggest that the NK1 receptor-positive projection neurons in lamina I are a major target of NO released in superficial dorsal horn. NO may also influence local circuit neurons, but it does not act on unmyelinated primary afferent terminals via sGC.
Figures




References
-
- Bellamy TC, Garthwaite J. The receptor-like properties of nitric oxide-activated soluble guanylyl cyclase in intact cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002;230:165–176. - PubMed
-
- Belyantseva IA, Lewin GR. Stability and plasticity of primary afferent projections following nerve regeneration and central degeneration. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:457–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

