Biochemical and functional characterization of the membrane association and membrane permeabilizing activity of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein
- PMID: 16507314
- PMCID: PMC7111751
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.01.028
Biochemical and functional characterization of the membrane association and membrane permeabilizing activity of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein
Abstract
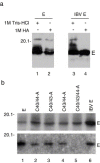
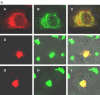
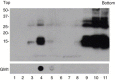
A diverse group of cytolytic animal viruses encodes small, hydrophobic proteins to modify host cell membrane permeability to ions and small molecules during their infection cycles. In this study, we show that expression of the SARS-CoV E protein in mammalian cells alters the membrane permeability of these cells. Immunofluorescent staining and cell fractionation studies demonstrate that this protein is an integral membrane protein. It is mainly localized to the ER and the Golgi apparatus. The protein can be translocated to the cell surface and is partially associated with lipid rafts. Further biochemical characterization of the protein reveals that it is posttranslationally modified by palmitoylation on all three cysteine residues. Systematic mutagenesis studies confirm that the membrane permeabilizing activity of the SARS-CoV E protein is associated with its transmembrane domain.
Figures
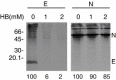

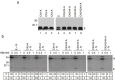


References
-
- Agirre A., Barco A., Carrasco L., Nieva J.B. Viroporin-mediated membrane permeabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:40434–40441. - PubMed
-
- Aldabe R., Barco A., Corrasco L. Membrane permeabilization by poliovirus proteins 2B and 2BC. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:23134–23137. - PubMed
-
- Bijlmakers M.-J., Marsh M. The on–off story of protein palmitoylation. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:32–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

