Gamma radiation increases endonuclease-dependent L1 retrotransposition in a cultured cell assay
- PMID: 16507671
- PMCID: PMC1385994
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkj522
Gamma radiation increases endonuclease-dependent L1 retrotransposition in a cultured cell assay
Abstract
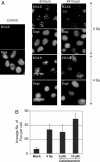
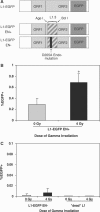
Long Interspersed Elements (LINE-1s, L1s) are the most active mobile elements in the human genome and account for a significant fraction of its mass. The propagation of L1 in the human genome requires disruption and repair of DNA at the site of integration. As Barbara McClintock first hypothesized, genotoxic stress may contribute to the mobilization of transposable elements, and conversely, element mobility may contribute to genotoxic stress. We tested the ability of genotoxic agents to increase L1 retrotransposition in a cultured cell assay. We observed that cells exposed to gamma radiation exhibited increased levels of L1 retrotransposition. The L1 retrotransposition frequency was proportional to the number of phosphorylated H2AX foci, an indicator of genotoxic stress. To explore the role of the L1 endonuclease in this context, endonuclease-deficient tagged L1 constructs were produced and tested for their activity in irradiated cells. The activity of the endonuclease-deficient L1 was very low in irradiated cells, suggesting that most L1 insertions in irradiated cells still use the L1 endonuclease. Consistent with this interpretation, DNA sequences that flank L1 insertions in irradiated cells harbored target site duplications. These results suggest that increased L1 retrotransposition in irradiated cells is endonuclease dependent. The mobilization of L1 in irradiated cells potentially contributes to genomic instability and could be a driving force for secondary mutations in patients undergoing radiation therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endonuclease-independent insertion provides an alternative pathway for L1 retrotransposition in the human genome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(11):3741-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm317. Epub 2007 May 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17517773 Free PMC article.
-
The Nucleotide Excision Repair Pathway Limits L1 Retrotransposition.Genetics. 2017 Jan;205(1):139-153. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.188680. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28049704 Free PMC article.
-
LINE-1 retrotransposition in human neuroblastoma cells is affected by oxidative stress.Cell Tissue Res. 2011 Dec;346(3):383-91. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1289-0. Epub 2011 Dec 10. Cell Tissue Res. 2011. PMID: 22160459
-
Progress in understanding the biology of the human mutagen LINE-1.Hum Mutat. 2007 Jun;28(6):527-39. doi: 10.1002/humu.20486. Hum Mutat. 2007. PMID: 17309057 Review.
-
A systematic analysis of LINE-1 endonuclease-dependent retrotranspositional events causing human genetic disease.Hum Genet. 2005 Sep;117(5):411-27. doi: 10.1007/s00439-005-1321-0. Epub 2005 Jun 28. Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15983781 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress Responses as Master Keys to Epigenomic Changes in Transcriptome and Metabolome for Cancer Etiology and Therapeutics.Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Jan 20;42(1):e0048321. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00483-21. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34748401 Free PMC article.
-
Role of long interspersed nuclear element-1 in the regulation of chromatin landscapes and genome dynamics.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Oct;246(19):2082-2097. doi: 10.1177/15353702211031247. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 34304633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombopoietin protects hematopoietic stem cells from retrotransposon-mediated damage by promoting an antiviral response.J Exp Med. 2018 May 7;215(5):1463-1480. doi: 10.1084/jem.20170997. Epub 2018 Apr 3. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29615469 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of LINE-1 and Alu retrotransposition by exosomes encapsidating APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F.Virology. 2010 Apr 25;400(1):68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.01.021. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Virology. 2010. PMID: 20153011 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic landscape of oxidative DNA damage and repair reveals regioselective protection from mutagenesis.Genome Biol. 2018 Dec 7;19(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1582-2. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 30526646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smit A.F., Toth G., Riggs A.D., Jurka J. Ancestral, mammalian-wide subfamilies of LINE-1 repetitive sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1995;246:401–417. - PubMed
-
- Lander E.S., Linton L.M., Birren B., Nusbaum C., Zody M.C., Baldwin J., Devon K., Dewar K., Doyle M., FitzHugh W., et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Moran J.V., Holmes S.E., Naas T.P., DeBerardinis R.J., Boeke J.D., Kazazian H.H., Jr High frequency retrotransposition in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1996;87:917–927. - PubMed
-
- Kazazian H.H., Jr Mobile elements and disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998;8:343–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

