Proteasome inhibitors induce a terminal unfolded protein response in multiple myeloma cells
- PMID: 16507771
- PMCID: PMC1895817
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3531
Proteasome inhibitors induce a terminal unfolded protein response in multiple myeloma cells
Abstract
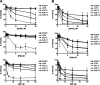
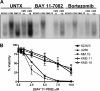
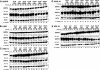
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable plasma cell malignancy. The 26S proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, selectively induces apoptosis in MM cells; however, the nature of its selectivity remains unknown. Here we demonstrate that 5 different MM cell lines display similar patterns of sensitivity to 3 proteasome inhibitors (PIs) but respond differently to specific NF-kappaB inhibition. We further show that PIs initiate the unfolded protein response (UPR), a signaling pathway activated by the accumulation of misfolded proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Consistent with reports that prosurvival/physiologic UPR components are required for B-cell differentiation into antibody-secreting cells, we found that MM cells inherently expressed the ER chaperones GRP78/Bip and GRP94/gp96. However, bortezomib rapidly induced components of the proapoptotic/terminal UPR, including PERK, the ER stress-specific eIF-2alpha kinase; ATF4, an ER stress-induced transcription factor; and its proapoptotic target, CHOP/GADD153. Consistent with our hypothesis that PIs induce the accumulation of misfolded ER-processed proteins, we found that the amount of immunoglobulin subunits retained within MM cells correlated with their sensitivity to PIs. These findings suggest that MM cells have a lower threshold for PI-induced UPR induction and ER stress-induced apoptosis because they constitutively express ER stress survival factors to function as secretory cells.
Figures

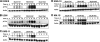

References
-
- Anderson KC. Bortezomib therapy for myeloma. Curr Hematol Rep. 2004;3: 65. - PubMed
-
- Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J Clin. 2000;50: 7-33. - PubMed
-
- Masdehors P, Omura S, Merle-Beral H, et al. Increased sensitivity of CLL-derived lymphocytes to apoptotic death activation by the proteasome-specific inhibitor lactacystin. Br J Haematol. 1999;105: 752-757. - PubMed
-
- Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, et al. Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 1999;59: 2615-2622. - PubMed
-
- Hideshima T, Richardson P, Chauhan D, et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and overcomes drug resistance in human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61: 3071-3076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

