Ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure are distinguished by their broad transcriptomic responses
- PMID: 16507785
- PMCID: PMC1502395
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00223.2005
Ischemic and nephrotoxic acute renal failure are distinguished by their broad transcriptomic responses
Abstract
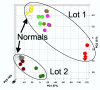
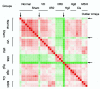
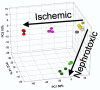
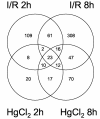
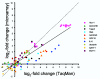
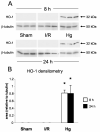
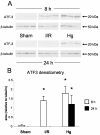
Acute renal failure (ARF) has a high morbidity and mortality. In animal ARF models, effective treatments must be administered before or shortly after the insult, limiting their clinical potential. We used microarrays to identify early biomarkers that distinguish ischemic from nephrotoxic ARF or biomarkers that detect both injury types. We compared rat kidney transcriptomes at 2 and 8 h after ischemia/reperfusion and after mercuric chloride. Quality control and statistical analyses were necessary to normalize microarrays from different lots, eliminate outliers, and exclude unaltered genes. Principal component analysis revealed distinct ischemic and nephrotoxic trajectories and clear array groupings. Therefore, we used supervised analysis, t-tests, and fold changes to compile gene lists for each group, exclusive or nonexclusive, alone or in combination. There was little network connectivity, even in the largest group. Some microarray-identified genes were validated by TaqMan assay, ruling out artifacts. Western blotting confirmed that heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and activating transcription factor-3 (ATF3) proteins were upregulated; however, unexpectedly, their localization changed within the kidney. HO-1 staining shifted from cortical (early) to outer stripe of the outer medulla (late), primarily in detaching cells, after mercuric chloride but not ischemia/reperfusion. ATF3 staining was similar, but with additional early transient expression in the outer stripe after ischemia/reperfusion. We conclude that microarray-identified genes must be evaluated not only for protein levels but also for anatomical distribution among different zones, nephron segments, or cell types. Although protein detection reagents are limited, microarray data lay a rich foundation to explore biomarkers, therapeutics, and the pathophysiology of ARF.
Figures




References
-
- Alam J, Killeen E, Gong P, Naquin R, Hu B, Stewart D, Ingelfinger JR, Nath KA. Heme activates the heme oxygenase-1 gene in renal epithelial cells by stabilizing Nrf2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;284:F743–752. - PubMed
-
- Amin RP, Vickers AE, Sistare F, Thompson KL, Roman RJ, Lawton M, Kramer J, Hamadeh HK, Collins J, Grissom S, Bennett L, Tucker CJ, Wild S, Kind C, Oreffo V, Davis JW, 2nd, Curtiss S, Naciff JM, Cunningham M, Tennant R, Stevens J, Car B, Bertram TA, Afshari CA. Identification of putative gene based markers of renal toxicity. Environ Health Perspect. 2004;112:465–479. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Bock C, Coleman M, Collins B, Davis J, Foulds G, Gold L, Greef C, Heil J, Heilig JS, Hicke B, Hurst MN, Husar GM, Miller D, Ostroff R, Petach H, Schneider D, Vant-Hull B, Waugh S, Weiss A, Wilcox SK, Zichi D. Photoaptamer arrays applied to multiplexed proteomic analysis. Proteomics. 2004;4:609–618. - PubMed
-
- Brooks HL, Ageloff S, Kwon TH, Brandt W, Terris JM, Seth A, Michea L, Nielsen S, Fenton R, Knepper MA. cDNA array identification of genes regulated in rat renal medulla in response to vasopressin infusion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;284:F218–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

