Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates diabetes-enhanced apoptosis of matrix-producing cells and impairs diabetic healing
- PMID: 16507891
- PMCID: PMC1606517
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050907
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates diabetes-enhanced apoptosis of matrix-producing cells and impairs diabetic healing
Abstract
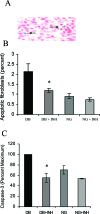
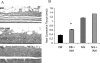
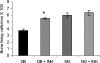
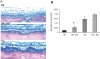
Diabetics suffer increased infection followed by increased apoptosis of fibroblasts and bone-lining cells during the healing process. To investigate a potential mechanism, we inoculated Porphyromonas gingivalis into the scalp of type 2 diabetic (db/db) or control mice and inhibited tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) with etanercept. Mice were euthanized at the early phase of infection (21 hours) or during the peak repair of the bacteria-induced wound (8 days). At 21 hours, TNF-alpha inhibition significantly reduced fibroblast apoptosis and caspase-3 activity in both diabetic and normoglycemic mice (P < 0.05). During healing etanercept reduced fibroblast apoptosis and caspase-3 activity by almost 50% in diabetic but not normoglycemic mice (P < 0.05). Concomitantly, etanercept significantly increased fibroblast number by 31% and new matrix formation by 72% in diabetic mice. When bone was examined during healing, administration of the TNF-alpha blocker reduced apoptosis of bone-lining cells by 53%, increased their number by 48%, and enhanced new bone formation by 140% in the diabetic group (P < 0.05). The degree of connective tissue and osseous healing stimulated in the diabetic mice by anti-TNF-alpha treatment was within the range that is physiologically relevant. This enhanced healing may in part be explained by block-ing TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis of critical matrix-producing cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diabetes enhances mRNA levels of proapoptotic genes and caspase activity, which contribute to impaired healing.Diabetes. 2006 Feb;55(2):487-95. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-1201. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16443785
-
TNF-alpha mediated apoptosis plays an important role in the development of early diabetic retinopathy and long-term histopathological alterations.Mol Vis. 2009 Jul 25;15:1418-28. Mol Vis. 2009. PMID: 19641635 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes alters the response to bacteria by enhancing fibroblast apoptosis.Endocrinology. 2004 Jun;145(6):2997-3003. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1601. Epub 2004 Mar 19. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15033911
-
Impaired wound healing in mouse models of diabetes is mediated by TNF-alpha dysregulation and associated with enhanced activation of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1).Diabetologia. 2010 Feb;53(2):378-88. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1529-y. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Diabetologia. 2010. PMID: 19902175 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting tumor necrosis factor alpha. New drugs used to modulate inflammatory diseases.Dermatol Clin. 2001 Oct;19(4):617-35. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8635(05)70304-1. Dermatol Clin. 2001. PMID: 11705350 Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetes reduces mesenchymal stem cells in fracture healing through a TNFα-mediated mechanism.Diabetologia. 2015 Mar;58(3):633-642. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3470-y. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 25563724 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced glycation end products stimulate osteoblast apoptosis via the MAP kinase and cytosolic apoptotic pathways.Bone. 2007 Feb;40(2):345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.09.011. Epub 2006 Oct 24. Bone. 2007. PMID: 17064973 Free PMC article.
-
Skin Inflammation with a Focus on Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2023 May;12(5):269-287. doi: 10.1089/wound.2021.0126. Epub 2022 May 26. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2023. PMID: 35287486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effect of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Attenuate Markers for Inflammation and Osteoclast Differentiation by Suppressing NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathway in Chronic Periodontitis.Molecules. 2021 Oct 30;26(21):6578. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216578. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770985 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Topical Therapy for Diabetic Wounds: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2023 Mar 29;15(3):e36887. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36887. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37128530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Klimiuk PA, Sierakowski S, Domyslawska I, Chwiecko J. Effect of repeated infliximab therapy on serum matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:238–242. - PubMed
-
- Catrina AI, Lampa J, Ernestam S, af Klint E, Bratt J, Klareskog L, Ulfgren AK. Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha therapy (etanercept) down-regulates serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 and MMP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41:484–489. - PubMed
-
- Krueger G, Callis K. Potential of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:218–225. - PubMed
-
- Graves DT, Cochran D. The contribution of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor to periodontal tissue destruction. J Periodontol. 2003;74:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Ardizzone S, Bianchi Porro G. Biologic therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. Drugs. 2005;65:2253–2286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

