Inhibitory role of CD19 in the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating cytokine response
- PMID: 16507897
- PMCID: PMC1606513
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050923
Inhibitory role of CD19 in the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating cytokine response
Abstract
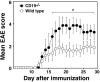
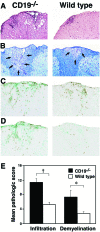
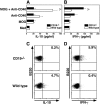
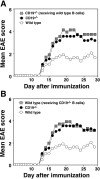
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nerve system that is considered a T helper type 1 (Th1)-mediated autoimmune disease. EAE currently serves as an experimental animal model for multiple sclerosis in human. Cytokines, such as interferon-gamma and interleukin-10, play a key role in the development and remission of EAE. Recent studies have also shown a role for B cells in the pathogenesis of EAE. Therefore, we examined the role of CD19, a B cell-specific surface molecule that defines signaling thresholds critical for B-cell responses and autoimmunity, on the development of EAE. Following immunization with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) peptide, CD19-deficient (CD19(-/-)) mice exhibited higher clinical and pathological severity scores of EAE than wild-type mice. The increased severity of EAE in CD19(-/-) mice was associated with polarized Th1 cytokines in the inflamed central nerve system but not with anti-MOG antibodies in the serum. MOG-primed CD19(-/-) B cells produced high levels of interferon-gamma, and transfer of MOG-primed CD19(-/-) B cells to wild-type mice worsened the disease. Thus, CD19 modulates the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance in B cells and plays a critical role as a suppressive molecule in the development of EAE.
Figures


References
-
- Fillatreau S, Sweenie CH, McGeachy MJ, Gray D, Anderton SM. B cells regulate autoimmunity by provision of IL-10. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:944–950. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein E, Peeva E, Putterman C, Diamond B. B-cell biology. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2004;30:159–174. - PubMed
-
- Chan OT, Madaio MP, Shlomchik MJ. B cells are required for lupus nephritis in the polygenic, Fas-intact MRL model of systemic autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1999;163:3592–3596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

