Posttranslational regulation of tristetraprolin subcellular localization and protein stability by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways
- PMID: 16508015
- PMCID: PMC1430283
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.6.2408-2418.2006
Posttranslational regulation of tristetraprolin subcellular localization and protein stability by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways
Abstract
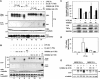
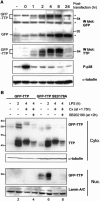
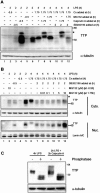
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, acting through the downstream kinase MK2, regulates the stability of many proinflammatory mRNAs that contain adenosine/uridine-rich elements (AREs). It is thought to do this by modulating the expression or activity of ARE-binding proteins that regulate mRNA turnover. MK2 phosphorylates the ARE-binding and mRNA-destabilizing protein tristetraprolin (TTP) at serines 52 and 178. Here we show that the p38 MAPK pathway regulates the subcellular localization and stability of TTP protein. A p38 MAPK inhibitor causes rapid dephosphorylation of TTP, relocalization from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, and degradation by the 20S/26S proteasome. Hence, continuous activity of the p38 MAPK pathway is required to maintain the phosphorylation status, cytoplasmic localization, and stability of TTP protein. The regulation of both subcellular localization and protein stability is dependent on MK2 and on the integrity of serines 52 and 178. Furthermore, the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway synergizes with the p38 MAPK pathway to regulate both stability and localization of TTP. This effect is independent of kinases that are known to be synergistically activated by ERK and p38 MAPK. We present a model for the actions of TTP and the p38 MAPK pathway during distinct phases of the inflammatory response.
Figures




References
-
- Blackshear, P. J., W. S. Lai, E. A. Kennington, G. Brewer, G. M. Wilson, X. Guan, and P. Zhou. 2003. Characteristics of the interaction of a synthetic human tristetraprolin tandem zinc finger peptide with AU-rich element-containing RNA substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 278:19947-19955. - PubMed
-
- Brewer, B. Y., J. Malicka, P. J. Blackshear, and G. M. Wilson. 2004. RNA sequence elements required for high affinity binding by the zinc finger domain of tristetraprolin: conformational changes coupled to the bipartite nature of Au-rich MRNA-destabilizing motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 279:27870-27877. - PubMed
-
- Bridges, D., and G. B. Moorhead. 2005. 14-3-3 proteins: a number of functions for a numbered protein. Sci. STKE 2005:re10. - PubMed
-
- Brook, M., G. Sully, A. R. Clark, and J. Saklatvala. 2000. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor alpha mRNA stability by the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 signalling cascade. FEBS Lett. 483:57-61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
