Crosstalk between the EGFR and other signalling pathways at the level of the global transcriptional corepressor Groucho/TLE
- PMID: 16508633
- PMCID: PMC2361374
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603019
Crosstalk between the EGFR and other signalling pathways at the level of the global transcriptional corepressor Groucho/TLE
Abstract
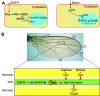
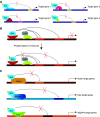
In this minireview, we briefly revisit the Drosophila Notch and epidermal growth factor receptor pathways, and relate to the relationship between them. We then mainly focus on the involvement of Groucho (Gro)/TLE, a global developmental corepressor, in these pathways. In particular, we discuss Gro/TLE's role at the junction between these two signal transduction cascades.
Figures
Republished in
-
Crosstalk between the EGFR and other signalling pathways at the level of the global transcriptional corepressor Groucho/TLE.Br J Cancer. 2007;96 Suppl:R21-5. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17393581
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

