Methodological study of affine transformations of gene expression data with proposed robust non-parametric multi-dimensional normalization method
- PMID: 16509971
- PMCID: PMC1534066
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-100
Methodological study of affine transformations of gene expression data with proposed robust non-parametric multi-dimensional normalization method
Abstract
Background: Low-level processing and normalization of microarray data are most important steps in microarray analysis, which have profound impact on downstream analysis. Multiple methods have been suggested to date, but it is not clear which is the best. It is therefore important to further study the different normalization methods in detail and the nature of microarray data in general.
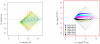
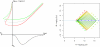
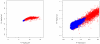
Results: A methodological study of affine models for gene expression data is carried out. Focus is on two-channel comparative studies, but the findings generalize also to single- and multi-channel data. The discussion applies to spotted as well as in-situ synthesized microarray data. Existing normalization methods such as curve-fit ("lowess") normalization, parallel and perpendicular translation normalization, and quantile normalization, but also dye-swap normalization are revisited in the light of the affine model and their strengths and weaknesses are investigated in this context. As a direct result from this study, we propose a robust non-parametric multi-dimensional affine normalization method, which can be applied to any number of microarrays with any number of channels either individually or all at once. A high-quality cDNA microarray data set with spike-in controls is used to demonstrate the power of the affine model and the proposed normalization method.
Conclusion: We find that an affine model can explain non-linear intensity-dependent systematic effects in observed log-ratios. Affine normalization removes such artifacts for non-differentially expressed genes and assures that symmetry between negative and positive log-ratios is obtained, which is fundamental when identifying differentially expressed genes. In addition, affine normalization makes the empirical distributions in different channels more equal, which is the purpose of quantile normalization, and may also explain why dye-swap normalization works or fails. All methods are made available in the aroma package, which is a platform-independent package for R.
Figures






References
-
- Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science. 1995;270(5235):467–470. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson H. Identification and normalization of plate effects in cDNA microarray data. Preprints in Mathematical Sciences 2002:28, Mathematical Statistics, Centre for Mathematical Sciences, Lund University, Sweden; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

