Evidence for a gene influencing heart rate on chromosome 5p13-14 in a meta-analysis of genome-wide scans from the NHLBI Family Blood Pressure Program
- PMID: 16509988
- PMCID: PMC1413518
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-7-17
Evidence for a gene influencing heart rate on chromosome 5p13-14 in a meta-analysis of genome-wide scans from the NHLBI Family Blood Pressure Program
Abstract
Background: Elevated resting heart rate has been shown in multiple studies to be a strong predictor of cardiovascular disease. Previous family studies have shown a significant heritable component to heart rate with several groups conducting genomic linkage scans to identify quantitative trait loci.
Methods: We performed a genome-wide linkage scan to identify quantitative trait loci influencing resting heart rate among 3,282 Caucasians and 3,989 African-Americans in three independent networks comprising the Family Blood Pressure Program (FBPP) using 368 microsatellite markers. Mean heart rate measurements were used in a regression model including covariates for age, body mass index, pack-years, currently drinking alcohol (yes/no), hypertension status and medication usage to create a standardized residual for each gender/ethnic group within each study network. This residual was used in a nonparametric variance component model to generate a LOD score and a corresponding P value for each ethnic group within each study network. P values from each ethnic group and study network were merged using an adjusted Fisher's combining P values method and the resulting P values were converted to LOD scores. The entire analysis was redone after individuals currently taking beta-blocker medication were removed.
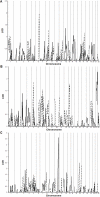
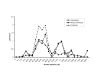
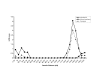
Results: We identified significant evidence of linkage (LOD = 4.62) to chromosome 10 near 142.78 cM in the Caucasian group of HyperGEN. Between race and network groups we identified a LOD score of 1.86 on chromosome 5 (between 39.99 and 45.34 cM) in African-Americans in the GENOA network and the same region produced a LOD score of 1.12 among Caucasians within a different network (HyperGEN). Combining all network and race groups we identified a LOD score of 1.92 (P = 0.0013) on chromosome 5p13-14. We assessed heterogeneity for this locus between networks and ethnic groups and found significant evidence for low heterogeneity (P < or = 0.05).
Conclusion: We found replication (LOD > 1) between ethnic groups and between study networks with low heterogeneity on chromosome 5p13-14 suggesting that a gene in this region influences resting heart rate.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evidence for a gene influencing heart rate on chromosome 4 among hypertensives.Hum Genet. 2002 Aug;111(2):207-13. doi: 10.1007/s00439-002-0780-9. Epub 2002 Jul 16. Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12189495
-
Quantitative trait loci on chromosome 8q24 for pancreatic beta-cell function and 7q11 for insulin sensitivity in obese nondiabetic white and black families: evidence from genome-wide linkage scans in the NHLBI Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network (HyperGEN) study.Diabetes. 2006 Feb;55(2):551-8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-0714. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16443794
-
Linkage analysis incorporating gene-age interactions identifies seven novel lipid loci: the Family Blood Pressure Program.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Jul;235(1):84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 24819747 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide linkage scans for fasting glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Family Blood Pressure Program: evidence of linkages to chromosome 7q36 and 19q13 from meta-analysis.Diabetes. 2005 Mar;54(3):909-14. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.3.909. Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 15734873
-
Genome-wide linkage analysis of lipids in the Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network (HyperGEN) Blood Pressure Study.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001 Dec;21(12):1969-76. doi: 10.1161/hq1201.100228. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11742872
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association analysis identifies multiple loci related to resting heart rate.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Oct 1;19(19):3885-94. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq303. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20639392 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association scan of RR and QT interval duration in 3 European genetically isolated populations: the EUROSPAN project.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009 Aug;2(4):322-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.108.833806. Epub 2009 May 15. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009. PMID: 20031603 Free PMC article.
-
Bivariate genetic association of KIAA1797 with heart rate in American Indians: the Strong Heart Family Study.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Sep 15;19(18):3662-71. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq274. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20601674 Free PMC article.
-
Heritability and linkage study on heart rates in a Mongolian population.Exp Mol Med. 2008 Oct 31;40(5):558-64. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.5.558. Exp Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18985014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dyer AR, Persky V, Stamler J, Paul O, Shekelle RB, Berkson DM, Lepper M, Schoenberger JA, Lindberg HA. Heart rate as a prognostic factor for coronary heart disease and mortality: findings in three Chicago epidemiologic studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1980;112:736–749. - PubMed
-
- Greenland P, Daviglus ML, Dyer AR, Liu K, Huang CF, Goldberger JJ, Stamler J. Resting heart rate is a risk factor for cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality: the Chicago Heart Association Detection Project in Industry. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;149:853–862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U10 HL054472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054496/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL51021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54464/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL54481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL47910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054464/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL045508/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54515/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054464/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54496/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL45508/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054496/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL054471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL051021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54509/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL054473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL54472/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

