Structures of a putative RNA 5-methyluridine methyltransferase, Thermus thermophilus TTHA1280, and its complex with S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
- PMID: 16511182
- PMCID: PMC1991318
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309105029842
Structures of a putative RNA 5-methyluridine methyltransferase, Thermus thermophilus TTHA1280, and its complex with S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
Abstract
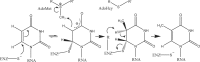
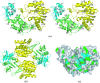
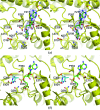
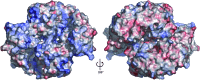
The Thermus thermophilus hypothetical protein TTHA1280 belongs to a family of predicted S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet) dependent RNA methyltransferases (MTases) present in many bacterial and archaeal species. Inspection of amino-acid sequence motifs common to class I Rossmann-fold-like MTases suggested a specific role as an RNA 5-methyluridine MTase. Selenomethionine (SeMet) labelled and native versions of the protein were expressed, purified and crystallized. Two crystal forms of the SeMet-labelled apoprotein were obtained: SeMet-ApoI and SeMet-ApoII. Cocrystallization of the native protein with S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine (AdoHcy) yielded a third crystal form, Native-AdoHcy. The SeMet-ApoI structure was solved by the multiple anomalous dispersion method and refined at 2.55 A resolution. The SeMet-ApoII and Native-AdoHcy structures were solved by molecular replacement and refined at 1.80 and 2.60 A, respectively. TTHA1280 formed a homodimer in the crystals and in solution. Each subunit folds into a three-domain structure composed of a small N-terminal PUA domain, a central alpha/beta-domain and a C-terminal Rossmann-fold-like MTase domain. The three domains form an overall clamp-like shape, with the putative active site facing a deep cleft. The architecture of the active site is consistent with specific recognition of uridine and catalysis of methyl transfer to the 5-carbon position. The cleft is suitable in size and charge distribution for binding single-stranded RNA.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwalla, S., Kealey, J. T., Santi, D. V. & Stroud, R. M. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277, 8835–8840. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L. & Koonin, E. V. (1999). J. Mol. Evol. 48, 291–302. - PubMed
-
- Brünger, A. T., Adams, P. D., Clore, G. M., DeLano, W. L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Jiang, J.-S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N. S., Read, R. J., Rice, L. M., Simonson, T. & Warren, G. L. (1998). Acta Cryst. D54, 905–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

