The production, purification and crystallization of a soluble form of the nonclassical MHC HLA-G: the essential role of cobalt
- PMID: 16511266
- PMCID: PMC2150919
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309105041473
The production, purification and crystallization of a soluble form of the nonclassical MHC HLA-G: the essential role of cobalt
Abstract
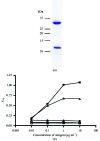
HLA-G is a nonclassical class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule that is primarily expressed at the foetal-maternal interface. Although the role of HLA-G has not been fully elucidated, current evidence suggests it protects the foetus from the maternal immune response. In this report, HLA-G (44 kDa) is characterized by expression in Escherichia coli. The inclusion bodies were refolded in complex with a peptide derived from histone H2A (RIIPRHLQL), purified and subsequently crystallized. Correct refolding was determined using two conformation-dependent antibodies. Cobalt ions were shown to be an essential ingredient for obtaining diffraction-quality crystals. The crystals, which diffracted to 1.9 A resolution, belonged to space group P3(2)2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = b = 77.15, c = 151.72 A.
Figures


References
-
- Allan, D. S., Lepin, E. J., Braud, V. M., O’Callaghan, C. A. & McMichael, A. J. (2002). J. Immunol. Methods, 268, 43–50. - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge, D., Ellis, S., Le Bouteiller, P. & Sargent, I. (2001). Trends Immunol.22, 548–552. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkman, P. J. & Parham, P. (1990). Annu. Rev. Biochem.59, 253–288. - PubMed
-
- Chapman, T. L., Heikeman, A. P. & Bjorkman, P. J. (1999). Immunity, 11, 603–613. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

