Structure of Lmaj006129AAA, a hypothetical protein from Leishmania major
- PMID: 16511295
- PMCID: PMC2197200
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309106005902
Structure of Lmaj006129AAA, a hypothetical protein from Leishmania major
Abstract
The gene product of structural genomics target Lmaj006129 from Leishmania major codes for a 164-residue protein of unknown function. When SeMet expression of the full-length gene product failed, several truncation variants were created with the aid of Ginzu, a domain-prediction method. 11 truncations were selected for expression, purification and crystallization based upon secondary-structure elements and disorder. The structure of one of these variants, Lmaj006129AAH, was solved by multiple-wavelength anomalous diffraction (MAD) using ELVES, an automatic protein crystal structure-determination system. This model was then successfully used as a molecular-replacement probe for the parent full-length target, Lmaj006129AAA. The final structure of Lmaj006129AAA was refined to an R value of 0.185 (Rfree = 0.229) at 1.60 A resolution. Structure and sequence comparisons based on Lmaj006129AAA suggest that proteins belonging to Pfam sequence families PF04543 and PF01878 may share a common ligand-binding motif.
Figures
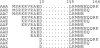

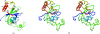
 6 (147–162). (b) Stereo figure depicted as a coil with every tenth residue numbered. It is in the same orientation and color scheme as (a).
6 (147–162). (b) Stereo figure depicted as a coil with every tenth residue numbered. It is in the same orientation and color scheme as (a).References
-
- Alexandrov, A., Vignali, M., LaCount, D. J., Quartley, E., de Vries, C., Rosa, D. D., Babulski, J., Mitchell, S. F., Schoenfeld, L. W., Fields, S., Hol, W. G., Dumont, M. E., Phizicky, E. M. & Grayhack, E. J. (2004). Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 3, 934–938. - PubMed
-
- Beitz, E. (2000). Bioinformatics, 16, 135–139. - PubMed
-
- Chayen, N. E., Shaw Stewart, P. D. & Blow, D. M. (1992). J. Cryst. Growth, 122, 176–180.
-
- Chivian, D., Kim, D. E., Malmström, L., Bradley, P., Robertson, T., Murphy, P., Strauss, C. E. M., Bonneau, R., Rohl, C. A. & Baker, D. (2003). Proteins, 53, 524–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

