Characterization of voltage-dependent sodium and calcium channels in mouse pancreatic A- and B-cells
- PMID: 16513675
- PMCID: PMC1780015
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.102368
Characterization of voltage-dependent sodium and calcium channels in mouse pancreatic A- and B-cells
Abstract
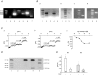
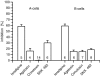
Insulin and glucagon are the major hormones of the islets of Langerhans that are stored and released from the B- and A-cells, respectively. Both hormones are secreted when the intracellular cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) increases. The [Ca2+]i is modulated by mutual inhibition and activation of different voltage-gated ion channels. The precise interplay of these ion channels in either glucagon or insulin release is unknown, owing in part to the difficulties in distinguishing A- from B-cells in electrophysiological experiments. We have established a single-cell RT-PCR method to identify A- and B-cells from the mouse. A combination of PCR, RT-PCR, electrophysiology and pharmacology enabled us to characterize the different sodium and calcium channels in mouse islet cells. In both A- and B-cells, 60% of the inward calcium current (I(Ca)) is carried by L-type calcium channels. In B-cells, the predominant calcium channel is Ca(v)1.2, whereas Ca(v)1.2 and Ca(v)1.3 were identified in A-cells. These results were confirmed by using mice carrying A- or B-cell-specific inactivation of the Ca(v)1.2 gene. In B-cells, the remaining I(Ca) flows in equal amounts through Ca(v)2.1, Ca(v)2.2 and Ca(v)2.3. In A-cells, 30 and 15% of I(Ca) is due to Ca(v)2.3 and Ca(v)2.1 activity, respectively, whereas Ca(v)2.2 current was not found in these cells. Low-voltage-activated T-type calcium channels could not be identified in A- and B-cells. Instead, two TTX-sensitive sodium currents were found: an early inactivating and a residual current. The residual current was only recovered in a subpopulation of B-cells. A putative genetic background for these currents is Na(v)1.7.
Figures



References
-
- Andrikopoulos S, Massa CM, Aston-Mourney K, Funkat A, Fam BC, Hull RL, et al. Differential effect of inbred mouse strain (C57BL/6, DBA/2, 129T2) on insulin secretory function in response to a high fat diet. J Endocrinol. 2005;187:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Proks P, Smith PA, Ammala C, Bokvist K, Rorsman P. Stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic beta cells. J Cell Biochem. 1994;55(Suppl.):54–65. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54:87–143. - PubMed
-
- Barg S. Mechanisms of exocytosis in insulin-secreting B-cells and glucagon-secreting A-cells. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003;92:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Barg S, Galvanovskis J, Gopel SO, Rorsman P, Eliasson L. Tight coupling between electrical activity and exocytosis in mouse glucagon-secreting alpha-cells. Diabetes. 2000;49:1500–1510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

