Fibrin derived from patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension is resistant to lysis
- PMID: 16514114
- PMCID: PMC2662971
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200506-916OC
Fibrin derived from patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension is resistant to lysis
Abstract
Rationale: Although acute pulmonary embolism is epidemiologically associated with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, the factors responsible for resistance to thrombolysis and a shift toward vascular remodeling within the pulmonary arteries of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension are unknown.
Objective: Determine whether fibrin from patients is more resistant to plasmin-mediated lysis than fibrin from healthy control subjects.
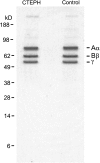
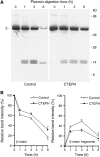
Methods: Fibrinogen purified from patients and control subjects was used to prepare fibrin clots, which were subsequently digested with plasmin for various periods of time. The degradation of the alpha-, beta-, and gamma-chains of fibrin and the appearance of peptide fragments over time were assessed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blotting.
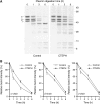
Measurements and main results: Densitometry of Coomassie-stained gels revealed significantly slower cleavage of all three polypeptide chains of fibrin from patients compared with control subjects (p < 0.05). In particular, release of N-terminal fragments from the beta-chain of fibrin, which promote cell signaling, cell migration, and angiogenesis, was retarded in patients compared with control subjects (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: The relative resistance of patient fibrin to plasmin-mediated lysis may be due to alterations in fibrin(ogen) structure affecting accessibility to plasmin cleavage sites. The persistence of structural motifs of fibrin, such as the beta-chain N-terminus, within the pulmonary vasculature could promote the transition from acute thromboemboli into chronic obstructive vascular scars.
Figures

References
-
- Fedullo PF, Auger WR, Kerr KM, Rubin LJ. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med 2001;345:1465–1472. - PubMed
-
- Wolf M, Boyer-Neumann C, Parent F, Eschwege V, Jaillet H, Meyer D, Simonneau G. Thrombotic risk factors in pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2000;15:395–399. - PubMed
-
- Olman MA, Marsh JJ, Lang IM, Moser KM, Binder BR, Schleef RR. Endogenous fibrinolytic system in chronic large-vessel thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 1992;86:1241–1248. - PubMed
-
- Lang IM, Marsh JJ, Olman MA, Moser KM, Schleef RR. Parallel analysis of tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma and endothelial cells derived from patients with chronic pulmonary thromboemboli. Circulation 1994;90:706–712. - PubMed
-
- Morris TA, Marsh JJ, Chiles PG. A possible etiology of chronic thrombo-embolic pulmonary hypertension [abstract]. Chest 2004;126:885S.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

