Heterologous expression of BetL, a betaine uptake system, enhances the stress tolerance of Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118
- PMID: 16517668
- PMCID: PMC1393183
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.3.2170-2177.2006
Heterologous expression of BetL, a betaine uptake system, enhances the stress tolerance of Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118
Abstract
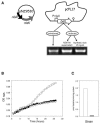
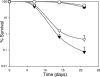
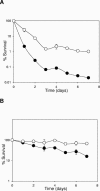
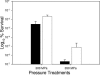
Given the increasing commercial and clinical relevance of probiotic cultures, improving the technological robustness of what are often process-sensitive cultures is an important biological goal. The nisin-controlled expression system was used to direct the heterologous expression of the listerial betaine uptake system BetL in the probiotic strain Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118. Following nisin induction, strains expressing betL exhibited a significant increase in resistance to several stresses, including elevated osmo-, cryo-, baro-, and chill tolerance, as well as increased resistance to spray- and freeze-drying. The ability to confer additional stress tolerance on a probiotic culture may be an important step in delivering viable cultures for maximal efficacy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A single point mutation in the listerial betL σ(A)-dependent promoter leads to improved osmo- and chill-tolerance and a morphological shift at elevated osmolarity.Bioengineered. 2013 Nov-Dec;4(6):401-7. doi: 10.4161/bioe.24094. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Bioengineered. 2013. PMID: 23478432 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the role of osmolyte transporters opuCA and betL in Listeria monocytogenes after cold and freezing stress.Arch Microbiol. 2017 Mar;199(2):259-265. doi: 10.1007/s00203-016-1300-y. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Arch Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27695911
-
Molecular and physiological analysis of the role of osmolyte transporters BetL, Gbu, and OpuC in growth of Listeria monocytogenes at low temperatures.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 May;70(5):2912-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.5.2912-2918.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15128551 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus salivarius and closely related Lactobacillus species.Future Microbiol. 2010 May;5(5):759-74. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.35. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20441548 Review.
-
Designer probiotics: Development and applications in gastrointestinal health.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015 Aug 15;6(3):73-8. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i3.73. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26301121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioengineered probiotics, a strategic approach to control enteric infections.Bioengineered. 2013 Nov-Dec;4(6):379-87. doi: 10.4161/bioe.23574. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Bioengineered. 2013. PMID: 23327986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of chemically defined media for Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis YF11 to eliminate the influence of hyperosmotic stress.3 Biotech. 2023 Nov;13(11):375. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03788-5. Epub 2023 Oct 21. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37873496 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Microbiome: Applications to Clostridium difficile Infection.J Clin Med. 2016 Sep 21;5(9):83. doi: 10.3390/jcm5090083. J Clin Med. 2016. PMID: 27657145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging importance of holobionts in evolution and in probiotics.Gut Pathog. 2013 May 22;5(1):12. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-5-12. Gut Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23694677 Free PMC article.
-
In a quest for engineering acidophiles for biomining applications: challenges and opportunities.Genes (Basel). 2018 Feb 21;9(2):116. doi: 10.3390/genes9020116. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29466321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abee, T., and J. A. Wouters. 1999. Microbial stress response in minimal processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 50:65-91. - PubMed
-
- Ananta, E., M. Volkert, and D. Knorr. 2005. Cellular injuries and storage stability of spray-dried Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Int. Dairy J. 15:399-409.
-
- Chandrapati, S., and D. J. O'Sullivan. 1999. Nisin independent induction of the nisA promoter in Lactococcus lactis during growth in lactose or galactose. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 170:191-198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

