Comparison of conventional PCR with real-time PCR and branched DNA-based assays for hepatitis C virus RNA quantification and clinical significance for genotypes 1 to 5
- PMID: 16517847
- PMCID: PMC1393102
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.44.3.729-737.2006
Comparison of conventional PCR with real-time PCR and branched DNA-based assays for hepatitis C virus RNA quantification and clinical significance for genotypes 1 to 5
Abstract
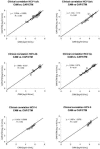
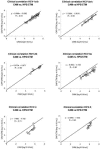
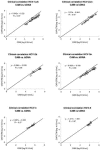
The key parameter for diagnosis and management of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is HCV RNA. Standardization of HCV RNA assays to IU is mainly based on genotype 1 panels. Little is known about the variability of commercially available HCV RNA assays for quantification of different genotypes. Two real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR assays (COBAS TaqMan HCV Test for use with the High-Pure System [HPS/CTM] and COBAS Ampliprep/COBAS TaqMan HCV Test [CAP/CTM]), one standard RT-PCR assay (COBAS Amplicor HCV Monitor 2.0 [CAM]), and one signal amplification assay (Versant Quantitative 3.0 [branched DNA [bDNA]]) were compared for quantification of genotypes 1 to 5 (n = 108). Using CAM as a reference assay for genotype 1-infected patients, the mean interassay differences compared with CAP/CTM, HPS/CTM, and bDNA were 0.16, -0.13, and -0.48 log(10) IU/ml HCV RNA, respectively. Comparison of CAM with CAP/CTM, HPS/CTM, and bDNA for the remaining genotypes showed the following results, respectively: 2a/c, -0.24, -0.78, and -0.49; 2b, -0.21, -0.18, and -0.64; 3a, 0.13, -1.04, and -0.55; 4, -0.52, -1.51, and -0.05; and 5, -0.28, -1.00, and -0.24 log IU/ml HCV RNA. A correct decision for treatment discontinuation in genotype 1 patients at week 12 was possible only when the same assay was used at baseline and week 12. Comparison of CAM with the CAP/CTM assay showed equal quantifications of genotype 1, 2, 3, and 5 samples, while genotype 4 samples were slightly underestimated. For the HPS/CTM assay, a significant underestimation of the HCV RNA concentrations of genotypes 2a/c, 3, 4, and 5 was observed. For the bDNA assay, a constant lower quantification of genotypes 1 to 3 was detected.
Figures
References
-
- Afdhal, N., E. Godofsky, J. Dienstag, V. Rustgi, L. Schick, D. McEniry, X. J. Zhou, G. Chao, C. Fang, B. Fielman, M. Myers, and N. Brown. 2004. Final phase I/II trial results for NM283, a new polymerase inhibitor for hepatitis C: antiviral efficacy and tolerance in patients with HCV-1 infection, including previous interferon failures. Hepatology 40(Suppl. 1):726A.
-
- Beld, M., R. Sentjens, S. Rebers, C. Weegink, J. Weel, C. Sol, and R. Boom. 2002. Performance of the new Bayer VERSANT HCV RNA 3.0 assay for quantitation of hepatitis C virus RNA in plasma and serum: conversion to international units and comparison with the Roche COBAS Amplicor HCV Monitor, version 2.0, assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:788-793. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berg, T., C. Sarrazin, E. Herrmann, H. Hinrichsen, T. Gerlach, R. Zachoval, B. Wiedenmann, U. Hopf, and S. Zeuzem. 2003. Prediction of treatment outcome in patients with chronic hepatitis C: significance of baseline parameters and viral dynamics during therapy. Hepatology 37:600-609. - PubMed
-
- Dalgard, O., K. Bjoro, K. B. Hellum, B. Myrvang, S. Ritland, K. Skaug, N. Raknerud, and H. Bell. 2004. Treatment with pegylated interferon and ribavarin in HCV infection with genotype 2 or 3 for 14 weeks: a pilot study. Hepatology 40:1260-1265. - PubMed
-
- Davis, G. L., J. B. Wong, J. G. McHutchison, M. P. Manns, J. Harvey, and J. Albrecht. 2003. Early virologic response to treatment with peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 38:645-652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

