Differentiating host-associated variants of Mycobacterium avium by PCR for detection of large sequence polymorphisms
- PMID: 16517871
- PMCID: PMC1393138
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.44.3.881-887.2006
Differentiating host-associated variants of Mycobacterium avium by PCR for detection of large sequence polymorphisms
Abstract
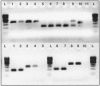
The Mycobacterium avium species consists of a group of organisms that are genetically related but phenotypically diverse, with certain variants presenting clear differences in terms of their host association and disease manifestations. The ability to distinguish between these subtypes is of relevance for accurate diagnosis and for control programs. Using a comparative genomics approach, we have uncovered large sequence polymorphisms that are, respectively, absent from bird-type M. avium isolates and from cattle types and sheep types of M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis. By evaluating the distribution of these genomic polymorphisms across a panel of strains, we were able to assign unique genomic signatures to these host-associated variants. We propose a simple PCR-based strategy based on these polymorphisms that can rapidly type M. avium isolates into these subgroups.
Figures

References
-
- Behr, M. A., M. Semret, A. Poon, and E. Schurr. 2004. Crohn's disease, mycobacteria, and NOD2. Lancet Infect. Dis. 4:136-137. - PubMed
-
- Behr, M. A., M. A. Wilson, W. P. Gill, H. Salamon, G. K. Schoolnik, S. Rane, and P. M. Small. 1999. Comparative genomics of BCG vaccines by whole-genome DNA microarray. Science 284:1520-1523. - PubMed
-
- Bull, T. J., E. J. McMinn, K. Sidi-Boumedine, A. Skull, D. Durkin, P. Neild, G. Rhodes, R. Pickup, and J. Hermon-Taylor. 2003. Detection and verification of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in fresh ileocolonic mucosal biopsy specimens from individuals with and without Crohn's disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:2915-2923. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chacon, O., L. E. Bermudez, and R. G. Barletta. 2004. Johne's disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 58:329-363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

