Evaluation of an automated seed loader for seed calibration in prostate brachytherapy
- PMID: 16518323
- PMCID: PMC5722483
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v7i1.2114
Evaluation of an automated seed loader for seed calibration in prostate brachytherapy
Abstract
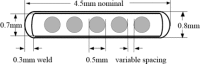
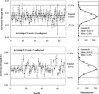
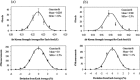
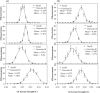
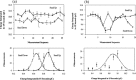
Automated seed loaders for permanent prostate implants are now commercially available. Besides improved radiation safety, these systems offer seed assay capability and ease of needle loading, making preplanned as well as intra-operative implant procedures more time-efficient. The Isoloader (Mentor Corp., CA) uses individual I125 seeds (SL-125 ProstaSeed) loaded in up to 199 chambers inside a shielded cartridge. The unit performs seed counting and calibration using a builtin solid-state detector. In order to evaluate the reproducibility and accuracy of the calibration process, two test cartridges were measured with the Isoloader itself and compared with a well-type ionization chamber (HDR-1000Plus, Standard Imaging). The air kerma strength measurements for all seeds using the Isoloader had a standard deviation of about 2.7%. For the eight seeds assayed more intensively using both the Isoloader and well chamber, the standard deviations of the measurements for each seed were in the range of 0.8% to 2.8% and 0.6% to 1.3%, respectively. The variation in the Isoloader calibration is attributed to small detector solid angle and bead geometry within seed capsules (verified by radiographs). The reproducibility of the air kerma strength measured by the Isoloader was comparable to that from the well chamber and was clinically acceptable. Seed strength measured with the Isoloader was on average 1% 2% larger than that measured with the well chamber, indicating that the accuracy of the Isoloader was clinically acceptable.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of an automatic needle-loading system.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2004 Spring;5(2):82-90. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v5i2.1971. Epub 2004 Apr 1. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2004. PMID: 15738915 Free PMC article.
-
Well-ionization chamber response relative to NIST air-kerma strength standard for prostate brachytherapy seeds.Med Phys. 2000 Oct;27(10):2293-6. doi: 10.1118/1.1290715. Med Phys. 2000. PMID: 11099196
-
Automated air kerma strength quality assurance of permanent seed implant prostate brachytherapy sources using vendor autoradiographs.Brachytherapy. 2019 Jul-Aug;18(4):539-545. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 May 4. Brachytherapy. 2019. PMID: 31064711
-
103Pd loaded cartridge air kerma strength verification.Med Dosim. 1999 Spring;24(1):73-5. doi: 10.1016/s0958-3947(98)00056-9. Med Dosim. 1999. PMID: 10100171
-
Robotic brachytherapy of the prostate.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2009;37(1-2):59-106. doi: 10.1615/critrevbiomedeng.v37.i1-2.20. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2009. PMID: 20201771 Review.
References
-
- Potters L. Permanent prostate brachytherapy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer. Clin Oncol. 2003;15:301–315. - PubMed
-
- Stock RG, Kao J, Stone NN. Penile erectile function after permanent radioactive seed implantation for treatment of prostate cancer. J Urol. 2001;165(2):436–439. - PubMed
-
- Morrier J, Varfalvy N, Chrétien M, Beaulieu L. Evaluation of an automated needle‐loading system. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2004;5(2):1–9, from http://www.jacmp.org - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kutcher GJ, Coia L, Gillin M, et al. Comprehensive QA for radiation oncology: Report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 40. Med Phys. 1994;21(4):581–618. - PubMed
-
- Li Z. Monte Carlo calculations of dosimetry of the Urocor Prostaseed source. Med Phys. 2002;29(6):1029–1034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

