Sepsis-induced organ failure is mediated by different pathways in the kidney and liver: acute renal failure is dependent on MyD88 but not renal cell apoptosis
- PMID: 16518342
- PMCID: PMC2271059
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000165
Sepsis-induced organ failure is mediated by different pathways in the kidney and liver: acute renal failure is dependent on MyD88 but not renal cell apoptosis
Abstract
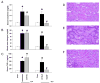
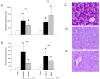
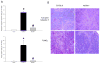
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are important in sepsis. Myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) is a key molecule involved in signal transduction by multiple TLRs. The objective of this study was to investigate the contribution of TLR4 and MyD88 to acute renal failure (ARF) induced by polymicrobial sepsis. Liver dysfunction and apoptosis in the spleen contribute to sepsis severity after cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Therefore, we also investigated liver injury and splenic apoptosis. We used a mouse model of sepsis-induced ARF using CLP to generate polymicrobial sepsis. Despite fluid and antibiotic resuscitation the mice developed multi-organ failure, including ARF, which resembles human sepsis. We investigated the role of the TLR4 receptor by comparing C3H/HeJ mice (which lack TLR4) with C3H/He0UJ normal controls. The role of MyD88 was investigated by comparing MyD88 knockout mice (MyD88(-/-)) with wild-type controls. Following CLP, mice lacking TLR4 and wild-type mice both developed comparable ARF. However, MyD88(-/-) mice did not develop ARF compared to wild-type controls. In contrast, MyD88(-/-) mice developed liver injury comparable to wild type. After CLP, MyD88(-/-) mice had significantly reduced apoptosis in the spleen compared with wild type. Apoptosis was not detected in the kidney of wild-type or MyD88(-/-) mice after CLP. In summary, ARF induced by polymicrobial sepsis is dependent on MyD88, but not TLR4. The absence of MyD88 dissociates ARF from liver injury; liver injury is MyD88-independent. There was MyD88-dependent apoptosis in the spleen, but no apoptosis in the kidney. MyD88 may be a good drug target for some, but not all, organ dysfunctions following sepsis.
Figures
References
-
- Schrier RW, Wang W. Acute renal failure and sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham PN, Wang Y, Guo R, et al. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in endotoxin-induced acute renal failure. J Immunol. 2004;172:2629–2635. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham PN, Dyanov HM, Park P, et al. Acute renal failure in endotoxemia is caused by TNF acting directly on TNF receptor-1 in kidney. J Immunol. 2002;168:5817–5823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

