Ultrasonography of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography and clinical examination
- PMID: 16519793
- PMCID: PMC1526591
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1904
Ultrasonography of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography and clinical examination
Abstract
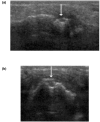
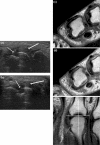
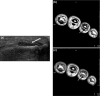
Signs of inflammation and destruction in the finger joints are the principal features of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). There are few studies assessing the sensitivity and specificity of ultrasonography in detecting these signs. The objective of the present study was to investigate whether ultrasonography can provide information on signs of inflammation and destruction in RA finger joints that are not available with conventional radiography and clinical examination, and comparable to the information provided by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The second to fifth metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints of 40 RA patients and 20 control persons were assessed with ultrasonography, clinical examination, radiography and MRI. With MRI as the reference method, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of ultrasonography in detecting bone erosions in the finger joints were 0.59, 0.98 and 0.96, respectively; they were 0.42, 0.99 and 0.95 for radiography. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of ultrasonography, with signs of inflammation on T1-weighted MRI sequences as the reference method, were 0.70, 0.78 and 0.76, respectively; they were 0.40, 0.85 and 0.72 for the clinical examination. With MRI as the reference method, ultrasonography had higher sensitivity and accuracy in detecting signs of inflammation and destruction in RA finger joints than did clinical and radiographic examinations, without loss of specificity. This study shows that ultrasonography has the potential to improve assessment of patients with RA.
Figures
References
-
- Konig H, Sieper J, Wolf KJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology. 1990;176:473–477. - PubMed
-
- Østergaard M. Magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Quantitative methods for assessment of the inflammatory process in peripheral joints. Dan Med Bull. 1999;46:313–344. - PubMed
-
- Ostendorf B, Peters R, Dann P, Becker A, Scherer A, Wedekind F, Friemann J, Schulitz KP, Modder U, Schneider M. Magnetic resonance imaging and miniarthroscopy of metacarpophalangeal joints: sensitive detection of morphologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2492–2502. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2492::AID-ART429>3.0.CO;2-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McGonagle D, Conaghan PG, O'Connor P, Gibbon W, Green M, Wakefield R, Ridgway J, Emery P. The relationship between synovitis and bone changes in early untreated rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1706–1711. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199908)42:8<1706::AID-ANR20>3.0.CO;2-Z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

