Dynamics of hip joint effusion after posterior soft tissue repair in total hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 16521013
- PMCID: PMC2532125
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-005-0064-9
Dynamics of hip joint effusion after posterior soft tissue repair in total hip arthroplasty
Abstract
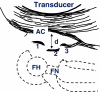
Dislocation after total hip replacement is more common in the early, postoperative period. Postoperative intraarticular haematoma and remaining seroma fluid and/or weakened posterior soft tissue wall may be contributing factors. Our purpose was to compare and follow with sonography the resorption of the postoperative volume of intraarticular fluid/synovial oedema after total hip arthroplasty (THA) with or without posterior soft tissue repair. Thirty-three consecutive patients with hip osteoarthritis were admitted for THA. All of them received the same type of cemented implant. Patients were randomised for posterior soft tissue repair or not. Sonography, measuring the anterior capsular distension, indicating the volume of intraarticular fluid/synovial oedema in the prosthetic hip joints, was performed after six and 12 months in all patients. At six months postoperatively greater capsular distension, i.e., remaining volume of intraarticular fluid/synovial oedema, was observed in the group with posterior soft tissue repair than in the group without. After one year the capsular distension had decreased in both groups and there was no significant difference between the groups. Our results show that posterior soft tissue repair after THA is associated with increased capsular distension during the first six months. After 12 months the volume of intraarticular fluid/synovial oedema is the same with or without posterior soft tissue repair.
La luxation après prothèse totale de la hanche est plus fréquente précocement, en période postopératoire. L’hématome intra-articulaire et /ou l’altération des tissus postérieurs peuvent être des facteurs de cette luxation. Nous avons étudiés par échographie la résorption postopératoire des fluides articulaires et de l’œdème synovial après arthroplastie totale de la hanche faite avec ou sans réparation des tissus postérieurs. 33 patients consécutifs, opérés avec le même type d’implant cimenté furent randomisés vis-à-vis de la réparation, ou non, des tissus postérieurs. L’échographie, mesurant la distension capsulaire antérieure a été faite après 6 et 12 mois chez tous les patients. A 6 mois de l’intervention une augmentation de la distension capsulaire c’est à dire du volume liquidien résiduel était observée dans le groupe avec réparation des tissus postérieurs comparé au groupe sans réparation. Après 1 an la distension décroît dans les deux groupes sans différence significative entre les deux.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The analysis of posterior soft tissue repair durability after total hip arthroplasty in primary osteoarthritis patients.Hip Int. 2015 Sep-Oct;25(5):420-3. doi: 10.5301/hipint.5000232. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Hip Int. 2015. PMID: 25952917
-
[The impact of capsular repair on the dislocation rate after primary total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective analysis of 1972 cases].Z Orthop Unfall. 2014 Apr;152(2):130-43. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1368209. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Z Orthop Unfall. 2014. PMID: 24760453 German.
-
Posterior Soft Tissue Repair After Primary THA is Durable at Mid-term Followup: A Prospective MRI Study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Oct;473(10):3183-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4380-0. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 26047646 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of the posterior approach with soft tissue repair for primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015 Feb;101(1):39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2014.10.015. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25620028 Review.
-
A posterior approach to primary total hip arthroplasty with soft tissue repair.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004 Jan;(418):162-7. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200401000-00026. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. PMID: 15043109 Review.
Cited by
-
Is soft tissue repair a right choice to avoid early dislocation after THA in posterior approach?BMC Surg. 2017 May 19;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12893-017-0212-3. BMC Surg. 2017. PMID: 28525999 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing Complications and Enhancing the Functional Outcome of Total Hip Arthroplasty without Increasing Operation Time by Repairing Posterolateral Soft Tissues.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Sep 15;2022:8364423. doi: 10.1155/2022/8364423. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. Retraction in: Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9804132. doi: 10.1155/2023/9804132. PMID: 36176926 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7418301', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7418301/'}]}
- Fackler CD, Poss R (1980) Dislocation in total hip arthroplasties. Clin Orthop 151:169–178 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/BF00241767', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00241767'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1502581', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1502581/'}]}
- Földes K, Gaal M, Balint P, Nemenyi K, Kiss C, Balint G, Buchanan W (1992) Ultrasonography after hip arthroplasty. Skeletal Radiol 21(5):297–299 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0883-5403(99)90116-X', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-5403(99)90116-x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10065717', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10065717/'}]}
- Kesteris U, Jonsson K, Robertsson O, Onnerfalt R, Wingstrand H (1999) Polyethylene wear and synovitis in total hip arthroplasty: A sonographic study of 48 hips. J. Arthroplasty 14(2):138–143 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2245542', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2245542/'}]}
- McCollum DE, Gray WJ (1990) Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: causes and prevention. Clin Orthop 261:159–170 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00003086-200403000-00027', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200403000-00027'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15057097', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15057097/'}]}
- Mihalko WM, Whiteside LA (2004) Hip mechanics after posterior soft tissue repair in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:194–198 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

