Sequence alignment by cross-correlation
- PMID: 16522868
- PMCID: PMC2291754
Sequence alignment by cross-correlation
Abstract
Many recent advances in biology and medicine have resulted from DNA sequence alignment algorithms and technology. Traditional approaches for the matching of DNA sequences are based either on global alignment schemes or heuristic schemes that seek to approximate global alignment algorithms while providing higher computational efficiency. This report describes an approach using the mathematical operation of cross-correlation to compare sequences. It can be implemented using the fast fourier transform for computational efficiency. The algorithm is summarized and sample applications are given. These include gene sequence alignment in long stretches of genomic DNA, finding sequence similarity in distantly related organisms, demonstrating sequence similarity in the presence of massive (approximately 90%) random point mutations, comparing sequences related by internal rearrangements (tandem repeats) within a gene, and investigating fusion proteins. Application to RNA and protein sequence alignment is also discussed. The method is efficient, sensitive, and robust, being able to find sequence similarities where other alignment algorithms may perform poorly.
Figures
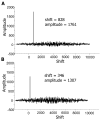
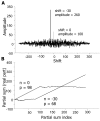
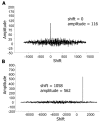
References
-
- Dayhoff MO, Eck RV, Park CM. Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure, vol. 5. Washington, DC: National Biomedical Research Foundation, 1972:75–84.
-
- Smith TF, Waterman MS. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol 1981;147:195–197. - PubMed
-
- Needleman SB, Wunsch CD. A general method applicable to search for similarities in the amino acid sequences of two proteins. J Mol Biol 1970;48:442–453. - PubMed
-
- Pearson WR. Effective protein sequence comparison. Methods Enzymol 1996;266:227–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
